MCHC Blood Test
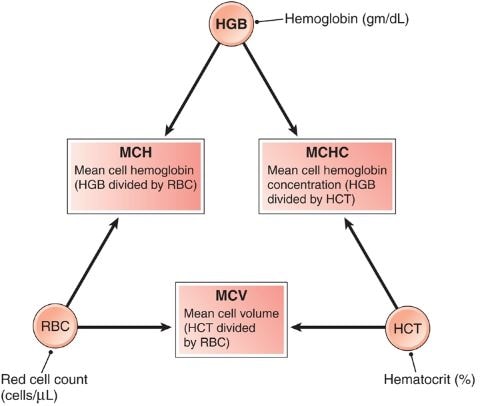
What is MCHC in blood test?
MCHC stands for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration. It is a measure of the hemoglobin concentration in a specific amount of red blood cells. In other words, MCHC is used to express the average or mean weight of hemoglobin within a given unit volume of RBC or red blood cell. Hemoglobin in blood is crucial because it helps in the transportation of oxygen within the vascular system. Hemoglobin also carries carbon dioxide, returning it back to your lungs.
Red blood cells are red in color because they contain traces of iron. Therefore, hemoglobin has iron traces. When the hemoglobin levels are fewer than normal, blood may not flow properly or in an efficient manner through your veins. Doctors will measure MCHC levels from the Complete Blood Count or CBC test. 1,2,3,4,5,6
The common reason of conduction of MCHC blood test is for assessment of macrocytic anemia and this test helps to calculate the hemoglobin content in the red blood cells. (1,2)
Why MCHC is Ordered By a Doctor?
A doctor will order a measurement of MCHC to help find out if a patient suffers from anemia. It may also be ordered if a doctor wants to know whether or not a patient has high levels of hemoglobin.
Calculation of MCHC
The calculation of MCHC is done by multiplying the obtainable numerical value of Hgb (hemoglobin) with 100 and then the value is divided by the amount of packed RBCs (this is also termed as hematocrit or Hct).
Therefore, (Hgb ÷ PCV or HCT) x 100
How to perform MCHC test?
The MCHC blood test is a part Complete blood count (CBC) test. For estimating the MCHC value, blood is withdrawn in a blood sample tube. Before withdrawing process has commenced, a certain amount of anti-coagulant is added to the tube.
Then collected blood sample is passed into a Coulter counter. Coulter counter has an orifice from where blood is passed through and the blood cell number and size are measured. The total number of RBC and their size are multiplied to get the result of hematocrit number.
Then the concentration of hemoglobin is also measured, when RBC becomes busted. Then automated instrument also calculate the MCHC value by dividing the hemoglobin amount by the hematocrit number. (4)
MCHC Levels – Normal, High, Low
To help find out the MCH levels in an individual, a doctor will order for CBC test. The normal levels of MCH in body are somewhere between 27 to 33 picograms per cell. However, the number may vary depending on what kind of machine has been used in doing the test. Again, the numbers may appear different in young kids. For a person to be said to have low MCH concentrations, the tests show levels of below 26 pg per cell. On the other hand, an individual is said to have high MCH levels if the concentrations are at 34 pg per cell and more.
High MCHC levels
If the MCHC value is more than 36%, then the result considers as MCHC value is higher than the normal. Having high levels of MCHC may be a sign of macrocytic anemia. With this condition, it occurs if the blood cells are excessively big. The larger size of the cells may be due to lack of sufficient folic acid or vitamin 12 in the body. There are other possible causes of high MCHC scores and they include:
Causes
There are various clinical causes responsible for high MCHC value. They are enlisted below:
- Macrocytic anemia. The symptoms of macrocytic anemia are severe fatigue, chronic headache, loose motion, uncontrolled body movement or ataxia, tongue soreness, breathing difficulty and increased heart rate or tachycardia.
- Spherocytosis is a rare hereditary disorder. In this disease condition, spherocytes, the abnormal cells present in the RBCs, which contains a large number of hemoglobin and causes higher value of MCHC.
- Deficiency of vitamin B12 is another cause of the high level of MCHC. Vitamin B12 or folic acid are essential for erythropoesis (the process of RBCs formation) and also for the maturation of RBCs, which content sufficient amount of hemoglobin.
- Liver disease also causes high MCHC, as the liver plays an important role in blood formation.
- In severely burn victim also has higher value of MCHC. (2,3,4)
- Drinking alcohol regularly
- Having an overactive thyroid gland
- Complications arising from some cancers
- Taking medications that contain estrogen
- Complications due to an infection.
Symptoms of High MCHC levels
Symptoms of high levels of MCHC may not be noticed at first but over time, they will become inherent. The symptoms include:
- Fast heartbeat
- Very pale skin
- Tiredness
- Memory loss and confusion
- Poor concentration and brain fog
- Brittle or easy to break nails
These symptoms are seen in persons with macrocytic anemia. A patient may also have digestive issues.
Low MCHC Levels
If the MCHC value is less than 28%, then clinically this is considered a low level of MCHC. The indication associated with this abnormal value is due to iron deficiency or hypochromic anaemia.
- Iron is an essential element of the hemoglobin. Deficiency of iron content causes abnormal and low content of the hemoglobin.
- Patients with hypochromic anemia have less number of hemoglobin in the red blood cells.
- Prolonged blood loss can also cause low value of MCHC. (2, 3,4)
Causes
Having low levels of MCHC may be caused by a number of things:
Anemia
Different types of anemia may result in low levels of MCHC. For instance, microcytic anemia, which occurs if a person has very small blood cells making them difficult to take in substantial amount of hemoglobin as needed. Often, microcytic anemia occurs due to nutritional deficiencies or malnutrition.
Reduced iron in blood
If there are low levels of iron in blood, that situation may cause low levels of MCHC. Iron is a mineral used by the body in making hemoglobin. So if there is insufficiency of this mineral, it may cause what is referred to iron deficient anemia, which in turn may contribute to reduced levels of MCHC. Iron deficient anemia is witnessed in people whose their main diet is vegetables or vegetarians, or people who have poor nutritional intake.
Celiac disease
Having health conditions like celiac disease may prevent proper absorption of iron and this makes it difficult for a person to have the required iron levels in body.
Gastric Surgery
If you have had gastric surgery, it may be responsible in impairing the absorption of iron.
Excessive menstruation
When a women has excessive menstruation, she may be anemic. They tend to lose a lot of iron through the menstrual blood and the body may not able to recover that.
Lack of vitamins
If you don’t get sufficient B vitamins including B12 and folate, it may bring about low MCHC levels.
Symptoms of Low MCHC levels
People having low levels of MCHC may not show symptoms at first, however, when these levels persist or they fall just too low, the patients will begin to show the symptoms. The symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Short of normal stamina
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness in body
- Consistent tiredness
- The skin may be pale or tends to bruise easily.
Diagnosis of MCHC Levels
In case a doctor suspects your MCHC levels to be high or low, a number of tests may be ordered. These include:
- A blood test to examine the level of MCHC
- An MCV test or mean corpuscular volume tests that is used to measure the average volume of red blood cells in blood sample.
The above tests can be part of the complete blood count or CBC test. Usually, a CBC tests is used to determine if red and white blood cells are in the normal ranges. From the tests ordered by a doctor, he or she will be able to find out exactly what anemia type you may have, and this makes it easy to determine the cause of the problem and the appropriate course of treatment to take.
Checking iron levels
The doctor may check the levels of iron in blood as well as the iron binding capacity. This helps determine if your body is absorbing iron in the way it is supposed to do. The checking of iron levels can be done from the blood sample that is used for checking CBC ranges. The tests may help the doctor to establish what the cause of anemia is.
Blood loss
A doctor may want to find out if blood loss may be causing low levels of MCHC score. Usually, the women who have heavy, long, or frequent menstrual periods may be detected easily for low levels of MCHC because they report that to the doctor during evaluation and check up.
If the doctor cannot ascertain what exactly is causing the low MCHC levels, they may order other tests. These include:
An endoscopy
In this examination, a doctor will use a lighted camera that is moved through the GI tract to find out if a patient may have cancer or ulcers. A biopsy test may be performed in this procedure to check for celiac disease.
An X-ray
A doctor may conduct X-ray on our upper GI to check for ulcers. A patient will drink a thick liquid that contains barium. The reason why barium is used in this X-ray is to help show if there are ulcers in the small intestine and stomach.
Other tests that the doctor may order are those used to screen a patient of Crohn’s or celiac disease.
Treatment of MCHC Levels
When the cause of having low levels of MCHC is determined by a doctor, a suitable treatment plan is put in place. The commonest cause of low levels of MCHC is anemia that is associated with iron deficiency. In treating iron deficiency anemia, a doctor will recommend treatment options such as:6
- Increasing your iron intake by taking foods rich in this substance such as spinach.
- Taking iron supplements
- Having more of vitamin B-6 that is necessary to ensure sufficient absorption of iron in body
- Having diet that is high in fiber to assist in the digestion and absorption of iron
- Checking your daily calcium intake as having too much of this mineral may impair the ability of the body to absorb iron.
For the case of high MCHC levels, a patient may need to take vitamin B12 as well as folic acid. The patient needs to take a balanced and varied diet containing these vitamins, but supplements may as well help the patient counter the high MCHC levels.
The systemic malfunctioning like defective bone marrow, malignancy, renal failure need to be corrected.
Certain medications can interfere with hemoglobin content, if so, then the immediate alteration of medication is needful to avoid serious health issues.
Nutritional deficiency, specifically iron, vitamin B12, folic acid and vitamin C cause abnormal MCHC value. This can be treated with supplementation. (4)

Reference List
- MCHC in Blood Tests: What Does it Mean & How to Test for It.(2013); Retrieve from: http://knowyourblood.com/mchc-in-blood-tests-what-does-it-mean-how-to-test-for-it/
- MCHC Blood Test Results Explained; Retrieve from: http://www.mchcbloodtest.com/
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration; MedFriendly; Retrieve from: http://www.medfriendly.com/mean-corpuscular-hemoglobin-concentration.html
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration – MCHC (2016); Retrieve from: http://coloncancer.about.com/od/glossary/g/MCHC.htm
- Yang Merritt (2014); Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC); Retrieve from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2054497-overview#a1
- Low MCHC Levels. Retrieved from http://www.healthline.com/health/low-mchc#causes3
- MCHC Blood Test: What It Means and What It Tells About Your Health. Retrieved from http://www.healthyandnaturalworld.com/mchc-blood-test/
- What is MCH? Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318192.php
