Haptoglobin
What is Haptoglobin?
Haptoglobin is a protein formed in your liver. It joins with hemoglobin, a protein found in your red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for transmitting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of your body. The bone marrow produces red blood cells, which are finally broken down in the liver and spleen.
When Haptoglobin is Formed?
When red blood cells are destroyed, they release hemoglobin, which is called free hemoglobin. Haptoglobin joins to the free hemoglobin to form a complex compound called haptoglobin-hemoglobin. This compound is transported to the liver where it is removed.
Your body usually maintains an equilibrium production and destruction of the red blood cells. When this balance is disrupted, red blood cells may be removed quickly than they are produced. This leads to drop in haptoglobin levels in your blood and can also cause hemolytic anemia.
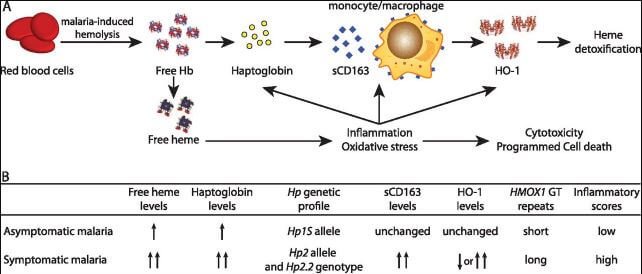
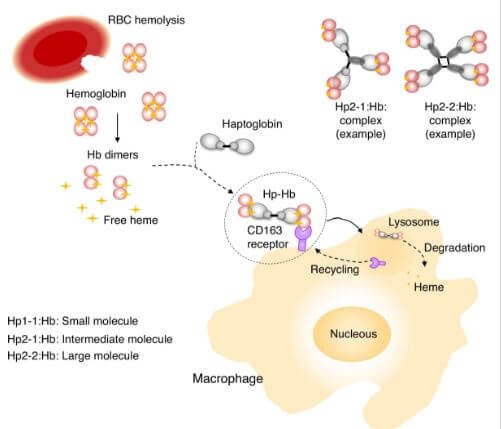
Haptoglobin Testing
A haptoglobin test can be conducted to determine the amount of Haptoglobin present in your blood. A haptoglobin test is carried out to detect and assess Hemolytic anemia and differentiate it from other forms of anemia. The test is done to determine whether your red blood cells are eliminated prematurely. Haptoglobin test may be used in combination with other tests such as:
Complete blood count
Complete blood count test is usually the first one a doctor conducts on you. It is done to find out the number of red blood cells, quantity of haemoglobin in blood and your blood level of haematocrit. Haematocrit level determines which percentage of your blood has red blood cells. Complete blood count test also assesses the size and shape of your red blood cells and the quantity of white blood cells in the blood.
Blood smear
This test is conducted to look for abnormal red blood cells in your blood.
Haptoglobin test cannot be used to diagnose the cause of hemolytic anemia. Other laboratory tests may be required to find out the cause of this condition because Hemolytic anemia has many causes such as
- Bone marrow tests
- Blood tests to determine any disease infection
- Tests to find out other conditions such as liver and kidney failure.
How is Haptoglobin Test done?
Haptoglobin test involves taking a sample of blood and assessing it. Your doctor or any health provider can take a sample of your blood. The sample of blood can be taken through the following steps:
Step 1: A health provider or your doctor will clean the area on your body where blood will be taken by a sterilizing solution.
Step 2: Then they will tie an elastic band around your arm to cause your veins to swell with blood and become visible. Once the vein is found, they will insert a needle into your vein to collect blood through a small tube or needle.
Step 3: When enough blood has been taken, the needle is removed and the area is covered with a bandage to stop further bleeding.
Haptoglobin test takes a short time to finish and you will receive results in few days.
What does a Haptoglobin Test Result mean?
The normal haptoglobin level is between 45 and 165 milligrams of haptoglobin per deciliter of blood. There are variations in haptoglobin level because of many factors such as the diagnostic facility and type of hospital used. If results show that your haptoglobin level is below 45 milligrams haptoglobin per deciliter of blood, it implies that your red blood cells are rapidly destroyed than they are formed.
This therefore, confirms that you have hemolytic anemia. Your doctor will explain what haptoglobin results mean. But, depending on the results, further tests are required to determine the cause of hemolytic anemia.
Elevated/High
If tests show that you have higher than normal levels of haptoglobin, it could indicate that you may have a health condition such as peptic ulcer, biliary obstruction, acute rheumatic disease, ulcerative colitis, or other inflammatory conditions.
Low
This may indicate that you have a health condition such as chronic liver disease, hematoma, idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia, primary liver disease, drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia, erythroblastosis fetalis, immune hemolytic anemia, or transfusion reaction.
Risks of Having Haptoglobin Test
Usually, there is little risk when having a blood sample taken for the test. Sometimes, the arteries and veins may vary from one individual to another and from one part of body to another part. So, at times, taking the blood sample may be difficult in some people than others. When drawing blood from a patients, there may occur:
- Fainting and feeling lightheaded
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection because the skin is broken
- Hematoma- where blood accumulates under your skin
- The laboratory technician taking the blood sample will ensure these risks are minimized.
Reference List
- Haemolytic Anaemia.http://www.medic8.com/blood-disorders/haemolytic-anaemia.htm
- Autoimmune disorders.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000816.htm
- Haemolytic Anemia.http://www.healthline.com/health/haemolytic-anemia#overview1
- Haptoglobin.http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/test/haptoglobin/overview.html
- Haptoglobin blood test.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003634.htm
- Haptoglobin.http://www.healthline.com/health/haptoglobin#overview1
