MCH Blood Test
What is MCH blood test?
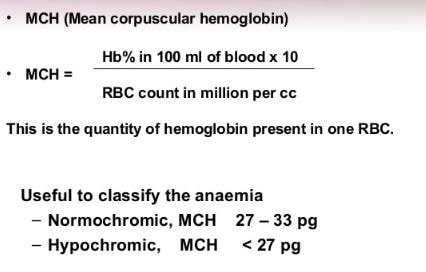
MCH blood test refers the average amount of hemoglobin present in the blood sample collected from the particular subject (human).
The MCH value is determined in the complete blood test (CBC), to estimates the hemoglobin, which is chief component of red blood cells for oxygen transportation in the every cells of the body.
Read – RDW Blood Test
The normal size of the RBC is denoted as normocytic, whereas increase size of the RBC refers as Macrocytic RBC and decrease size of the RBC is refers as microcytic RBC. The MCV value is greater than normal for Macrocytic RBC and the MCV value is lower than normal for microcytic RBC. (1, 2)
Read – MPV Blood test
What does MCH mean in a blood test?
MCH is used as clinical abbreviation used to refer mean corpuscular hemoglobin. By estimating this, the amount of hemoglobin present in the blood can be evaluated in blood test. (1,3)
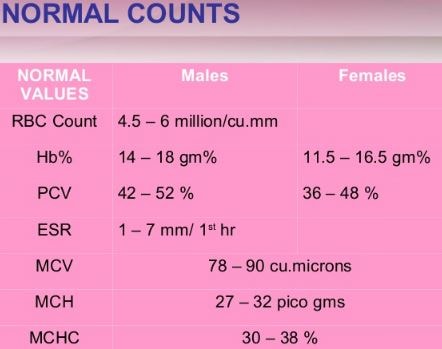
Normal values
The unit used to measure MCH level is picogram used to measure very small amount of weight. Picogram refers to one trillionth of a gram. The normal value of MCH is expressed in a range, which can vary from laboratory to laboratory due to difference in technical method or machine use for conduction of blood test.
The every lab report contains the normal value, which is followed in that particular clinical laboratory. This value is also varied with gender, as men are having more hemoglobin content than women.
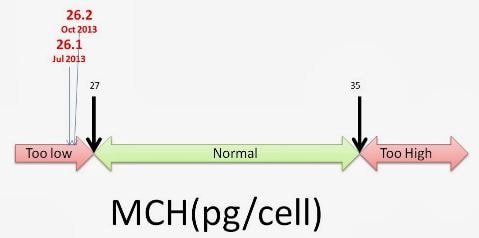
The normal range of 27 – 33 picograms of haemoglobin/ red blood cells. (4,5)
MCH blood test high
If the MCH value is more than 34 picograms, then it is medically considered the high value of MCV. This abnormal value is associated with macrocytic anemia. In this blood disorder, the amount of RBCs is less, but size of each cell is larger than the normal and each RBC also contains more hemoglobin content than the normal.
This clinical condition arises due to deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, as these two nutrients are essential for erythropoietin (production of RBC). In some individual, sufficient intake of vitamin B12 and folic acid may cause macrocytic anemia due to gastrointestinal disorders.
Causes of High MCH Value
Other possible causes to produce high MCH value are
- Dysfunction of thyroid hormone
- Anemia
- Chemotherapy
- Certain microbial infection
- Excessive use of estrogen-containing drugs
- Leukemia
- Genetic disorders such as spherocytosis
Symptoms of High MCH value
The usual symptoms associated with high MCH are cardiac complications like increase heart rate, palpitations, unusual tiredness, difficulty in breathing, skin coloration become pale, anorexia, diarrhea, soreness in the tongue.
Treatment of High MCH Value
To treat high level of MCH value need medical consultation with a doctor. Depending upon medical history and other test reports the underlying cause must be determine before initial any treatment. usually vitamin B12 or folic acid supplementation are require to treat the condition.
MCH blood test low
If the value of MCH is less than 26 picograms, then the condition is denoted as low MCH.
Causes of Low MCH Value
The possible causes associated with this condition are as follows:
- Acute or chronic hemorrhage
- Distorted molecular structure of hemoglobin
- The size of the RBC is less than the normal (microcytic anemia), means the low content of hemoglobin
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Celiac disease, which prevents the absorption of iron.
- Vitamin C deficiency, as it helps to absorption of iron.
- Surgical interventions of gastrointestinal tract.
The usual cause of distortion of molecular structure of hemoglobin or microcytic RBC is due to iron deficiency. Iron is a key element of hemoglobin molecular structure and oxygen transportation is main function of hemoglobin. Lack of hemoglobin can cause tissue necrosis due to deficit of oxygen supply.
Treatment of Low MCH Blood Test
The treatment approach is based on the underlying cause. The iron deficiency can be rectified by taking iron rich food items, including dry fruits, green vegetables, eggs, etc.
Other than these doctors may prescribe iron supplementation, but it may cause constipation or tarry colored stool. Along with iron, increase intake of citrus fruits rich in vitamin C like kiwi, strawberries, melon and included vegetables broccoli, tomatoes help in iron absorption. Oral vitamin C tablets are also available in pharmacy store.
References
- DaniellaNicole (2014); What Does a High MCH Level Mean in Blood Tests?; Retrieve from: http://www.brighthub.com/science/medical/articles/71162.aspx
- http://www.medfriendly.com/mean-corpuscular-hemoglobin.html
- Beth Greenwood (2014); What Is the Nutritional Significance of Low MCH and Low MCHC?; Retrieve from: http://www.livestrong.com/article/552363-what-is-the-nutritional-significance-of-a-low-mch-and-a-low-mchc/
- High MCH; Retrieve from: http://www.newhealthguide.org/High-Mch.html
- Todd Gersten; (2014); RBC indices; Retrieve from: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003648.htm
- Worried about High MCH Results in your Blood Test? Learn the Facts; Retrieve from: http://www.healthtestingcenters.com/what-does-a-high-mch-blood-test-result-mean.aspx
