Trigeminal Neuralgia
What is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a neurological disorder associated with facial pain. The trigeminal nerve is a cranial nerve and primly affected. Trigeminal nerve is subdivided into 12 parts, which divide into three branches. They carry impulses from upper, middle and lower facial parts including forehead, cheeks, gums, and teeth, side of the nose, upper lip, and upper jaw as a network and send it to the brain. Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic condition, but available medical treatments can able to control the pain.
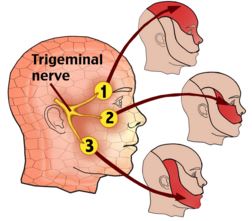
Image 1: Anatomy of Trigeminal Nerves
Trigeminal Neuralgia Causes
- The cause of the development of the trigeminal neuralgia is pressing of the blood vessels in the brain stem. This pressing of blood vessels leads to damage of the nerve covering or myelin sheath which protects the nerve.
- The multiple sclerosis disease also a reason behind the development of trigeminal neuralgia.
- Tumour formation in the trigeminal nerve can also compress the trigeminal nerve.
- Knot formation or twisting of arteries and veins, termed as arteriovenous malformation can be a cause of the trigeminal neuralgia development.
- Facial injuries, which include surgical process in the oral cavity, sinusitis surgery, and accidental trauma development in the facial region, may cause trigeminal neuralgia.
The triggering factors which aggravate the trigeminal neuralgia are:
- The activities where shaking or touching of the cheeks are common like during shaving, putting makeup on the face and face washing.
- Talking
- Brushing of teeth
- Chewing of food
- Drinking
- Direct contact with wind
Trigeminal Neuralgia Symptoms
The personal and social life is too much hampered, as the person with trigeminal neuralgia has always the anxiety during talking, eating and drinking, as the onset of pain is sudden and severe and may stay for a few minutes and even it lasts for a few hours to months. Previous indication or duration of pain is not fixed in trigeminal neuralgia. The following symptoms are often common with trigeminal neuralgia:
- Pain is sudden and shooting like feeling are felt on the face.
- Triggering factors cause impulsive attacks.
- In chronic cases, burning sensation and aching of feelings are prominent.
- Rarely attacks of short term pain arise during sleeping at night.
- The typical characteristics of trigeminal neuralgia are
- Continuous pain cannot arise, but after each interval the intensity of the pain increases.
- One side facial pain, rarely both sides are involved.
- Pain arises from a certain point and gradually extended into other parts
- Pain is not fatal, but can be debilitate person’s activities.
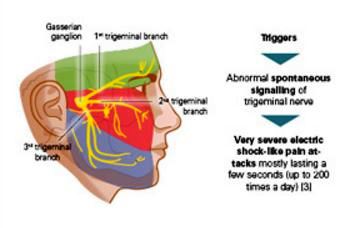
Image 2: Development and symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal Neuralgia Diagnosis
Initial diagnosis is based on symptomatic analysis, which involved:
- The areas where pain arises and extended – this identification is required to judge the involvement of trigeminal nerves.
- Description of pain is important, as the pain in trigeminal neuralgia has specific characteristics like sudden onset and shock like feelings.
- Triggering factors affect to worsen the conditions or not.
After taking the brief introduction about the pain description, for confirming the disorder, doctors recommend following diagnostic tests:
- Neurological test: This involves physical examination of the affected area and to identify which branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved. Reflex test also helps to determine that may either cause involve in pain generation or not.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain conduction gives the confirmation about the involvement of brain tumour or multiple sclerosis which can be a cause of trigeminal neuralgia.
- By using the dye, magnetic resonance angiogram test able to identify the affected blood vessels, which press the trigeminal nerve.
Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment
Medications are available to treat the trigeminal neuralgia, some patients responding good and medications are effective for them. Some patient has mild symptoms and may not require continuous drug therapies. In some cases, the available medications cannot be useful, due to long term use of these drugs cause drug resistance or some may discontinue the drug due to side effects of the medications. Treatment of underlying cause like multiple sclerosis treatment can improve the trigeminal neuralgia.
The available treatments require regular follow up and close monitoring of the condition, as they are having vast side effects and resistance grow capacity. To overcome these doctors are not stuck in a particular medicine for a long time, they are usually switching the therapy or adjusting the dose to overcome these problems.
The available medicines are as follows:
- Anti-seizure drugs: Doctors usually prescribe anti-seizures drugs alone or in combination. The preferable generic products available to treat the conditions are carbamazepine , oxcarbazepine and phenytoin. Other medicines which are also prescribed, including gabapentin and clonazepam.
- Muscle relaxing agents: These are prescribed alone or may be combined with carbamazepine. These drugs are beneficial for lowering the muscular spasms. Monitoring of side effects is important for therapy.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injection: Research gives the evidence that Botox injection can lessen the pain, but the more practical investigation is required to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Surgery
Two surgical processes involve for correcting trigeminal neuralgia:
Microvascular decompression
The involved blood vessels which compressing the trigeminal nerve are removed or adjusting the location, so that they cannot press the trigeminal nerve.
Gamma Knife radio-surgery
In this process radiation therapy damages the affected branch of the trigeminal nerve; this is beneficial for the reduction of the pain.
Balloon compression
By inserting a flexible catheter with a balloon at the root of the affected trigeminal nerve and then bursting the balloon. This helps to block the pain signalling.
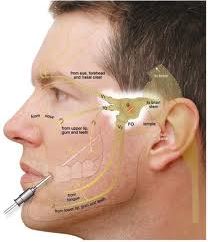
Image 3: surgical intervention in Trigeminal Neuralgia
References
- Trigeminal Neuralgia causes, symptoms, treatment at http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trigeminal-neuralgia/basics/definition/con-20043802
- http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/trigeminal_neuralgia/detail_trigeminal_neuralgia.htm
- http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/guide/trigeminal-neuralgia
- What is Trigeminal Neuralgia – http://fpa-support.org/trigeminal-neuralgia/
- http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Trigeminal-neuralgia/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Background, Anatomy at http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1145144-overview
