Otalgia
What is Otalgia?
Otalgia refers to the pain in the ears or earache; it is the pain that is felt in the outer part of the ears and inside the ears that occur due to several causes. There are two types of otalgia; depending on its site origin where the pain sensation is felt. The first type is primary otalgia; the pain here comes from the external, middle and inner part of the ear.
Primary otalgia is a symptom of another ear disease condition like external otitis, viral myringitis, acute otitis media and mastoiditis. The second type is called referred otalgia, where the ear pain sensation originates from other parts of the body, excluding the ears.
The ears are loaded with sensory innervations derived from four cranial nerves; the CN V (Trigeminal Nerve), CN VII (Facial Nerve), CN IX (Glossopharyngeal Nerve) and the CN X (Vagus Nerve); and two spinal segments. the C2 and C3, all of these nerves have distribution effect on the ears. When these specific nerves are affected by certain disease condition, it causes pain sensation within the ears.
Symptoms
Sign and symptoms include sensation of fullness in the ears or pain in the ear. The person who is having an earache has the following clinical manifestations; insomnia due to constant pain in the ears that interrupts sleep cycle, irritability due a nuisance of earache. Among children, one indicator is the persistent pulling of the affected ears. In severe cases, there will be a loss of balance, since our ears also function as balance organ coordinating with body movements.
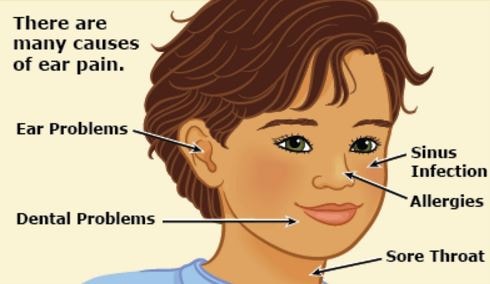
Causes
The occurrence of otalgia is due to the presence of other underlying disease condition; it can be primary and referred otalgia. The common cause for primary otalgia is acute otitis media; this is an infection in the middle ear secondary to conjunctivitis, cough and colds.

Other causes of primary otalgia are external otitis, viral myringitis, foreign body in the ears and mastoiditis. While in referred otalgia, dental disorder is a most common cause. Dental disease such as dental carries, periapical periodontitis, impacted third molar teeth and pulpitis.
This causes pain sensation in the ears because the oral cavity which is referred as an auriculotemporal nerve; a branch of trigeminal nerve, unfortunately. it is one of the sensory innervations of the ears that allows the person to feel the pain.
Another common cause of referred otalgia is sinusitis. The nasal cavity is also referred as an auriculotemporal nerve; a branch of trigeminal, where when nasal obstruction and sinus irritation occur, pain symptoms in the ears may develop.
Other referred causes are tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, laryngeal tumors, esophagitis, neuralgias and temporomandibular dysfunction. Traveling and scuba diving may also lead to referred otalgia; it alters the external pressure that can cause ear pain. In rare cases psychogenic otalgia happens, there is specific cause why pain in the ears is felt, but it could be a psychosomatic condition.
Treatment
Otalgia is best managed through comprehensive history taking and meticulous physical assessment should be done, to know the causative etiology of otalgia and to come up with the right diagnosis, for better and effective treatment.
History taking includes getting the right information starting from the chief complaints; the present illness; the patient experience like colds, trauma or injury; cardiopulmonary disease, swallowing difficulties, sinusitis, or any other otologic symptomatology for the last six months.
Past history taking can help direct the physician in choosing the succeeding test for diagnosis.
Physical examination includes:
- Comprehensive head to toe assessment
- Inspection of ears by the use of otoscope
- Checking auditory acuity and lateralization by Weber and Rinne test by the use of tuning pork.
- Laryngoscopy
- Endoscopy
- Nasopharyngoscopy
- MRI
- Rhinoscopy
- X-rays
- CT scan
If the causative disease is already determined or if it’s primary or referred otalgia, treatment of choice will depend on the underlying problem. Primary otalgia is usually treated with antibiotics if the causative agent is bacteria, antifungal for fungus and antiviral for suspected virus.
For referred otalgia, the specific underlying cause should be identified first and consult a specialist for the treatment course that will be needed to relieve the otalgia.
Otalgia is usually treated with age appropriate analgesic or topical anesthetic agent for sensitive ear canal, as prescribed by an attending physician.
During the diagnosis, the use of any analgesic, narcotics or NSAIDs will be put on hold, because it mask symptoms making it hard to find out the underlying problem. Patients with such condition are supposed to undergo episodes of reevaluation and kept under observation.
It has to be remembered well that it is very significant to complete and comply the prescribed treatment of an otalgia, especially when it involves medicines that are antibacterial, antifungal or with an antiviral effect. For home remedy, putting a warm washcloth to the affected ears will also relieve the pain, chewing a gum and keeping the mouth moving helps relieve the pain since it activates the muscle in the ears.
ICD code 9
Here are 2014 ICD 9 – Cm Diagnosis Codes:
- Diseases of the Nervous systems and sense organs
http://www.icd9data.com/2014/Volume1/default.htm
- Diseases of the Ear and Mastoid Process
http://www.icd9data.com/2014/Volume1/320-389/default.htm
- Other disorders of the ears
http://www.icd9data.com/2014/Volume1/320-389/380-389/default.htm
References
Source:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Otalgia
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/845173-overview
- http://patient.info/doctor/otalgia-earache
Books:
- Y. Sharav & R. Benoliel, (2008). Orofacial Pain and Headache
- G. B. Hughes & M. L. Pensak, ( 2011). Clinical Otology
- F. E. Lucente & G. Har-El, (2004). Essentials of Otolaryngology
