Toenail Fungus
Some fungi is considered to be a part of the normal flora outside of the body, but if it overgrows, it can cause an infection to the body part that is affected. The nails is one of the most common areas that is affected by fungal overgrowth [1, 2].
Anatomy and Physiology of Toenail
Toenails are horny cutaneous plates that grow away from the nail base. They are composed of epithelial scales that developed from the skin’s stratum lucidum. Toenails provide protection to the nail bed and any damage to the integrity of this area may cause a permanent and significant deformity on the growth of the toenail [3, 4].
Fungi overgrowth on the toenails is also known as onychomycosis and tinea unguium. The overgrowth occurs more often in the toenails because of they are usually confined inside a shoe. This condition creates a warm and humid environment that is ideal for fungi to thrive. The type of fungi that causes toenail fungus is also the same ones that cause athlete’s foot, jock itch and ringworm. Yeasts and molds can also cause toenail infection [2, 3].
The growth of fungi happens very slowly so it may not be noticeable at first. It typically begins as a yellow or white spot that is found under the tip of the toenail. As the fungi continuously grow, the infection will go deeper into the nail and may cause thickening and discoloration of the toenail. It will also begin to crumble at the edges. It may affect a single or several nails but it rarely affects all of the toenails [2, 3].
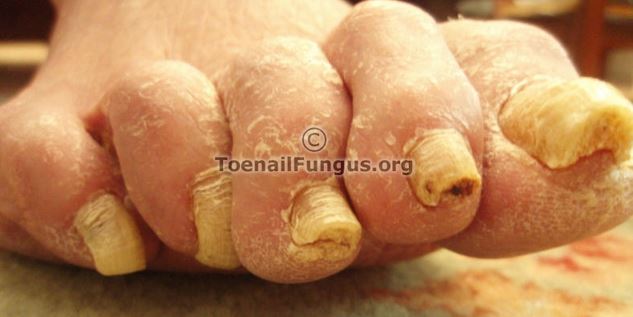
Figure 1 shows an example of a toenail fungus.
ICD10
Based on the 2016 ICD-10-CM diagnosis handbook, the code that is used for toenail fungi is B35.1. This is for a fungal infection of the nail that may be caused by dermatophytes, yeasts or nondermatophyte molds [5].
Causes of Toenail Fungus
In healthy people, the fungi that causes the infection are the ones that thrive in moist and warm areas. The usual places where this type of fungi can be contracted are swimming pools and communal showers. An individual who gets a manicure or pedicure in a nail salon where the tools are not sanitized may also get the fungus. Unsanitized nail clippers and emery boards can spread the fungi infection from one individual to another [1, 2, 6].
Risk Factors of Toenail Fungus
Although some of the causes of toenail fungus may be prevented, there are some risk factors that increases the chance of an individual to acquire the infection. An older individual who have reduced blood flow secondary to diabetes or any condition that causes poor circulation is at risk because of the greater number of years that he is exposed to the fungus.
Working in an environment where there is high humidity or in a job where the foot is always wet becomes a risk because this is an ideal environment for the fungi to grow. Living with a person who has a toenail fungi is not uncommon and this may spread to other people in the household [1, 2].
Having a concurrent fungal infection such as athlete’s foot or jock itch increases the likelihood because of the presence of fungi. Skin conditions that causes break in the body’s defense such as psoriasis makes it easy for the fungi to invade the skin and toenails [1, 2].
Signs and Symptoms of Toenail Fungus
A toenail that is affected by a fungal infection may have the following characteristics [1, 2]:
- Streaks of white or yellow on the nail (Onychomycosis)
- Scaling under the nail (Subungal hyperkeratosis)
- Development of yellow spots at the bottom part of the nail (Proximal onychomycosis)
- Crumbling on the corner or the tip of the nail (Distal onychomycosis)
- A bad odor coming from the infected nails
- Flaking white areas found on the surface of the nail
- Distortion of the nail where it may be lifted away from the nail bed
- Nail loss
Diagnosis
Health history and physical examination
A physician should be consulted once change in one’s hygiene was not able to improve the condition of the skin. The focus of the history is to identify the date when the symptoms have started appearing and the presence of any risk factors for toenail fungus. In the physical examination, the condition of the toenails will be examined [1, 2, 4].
Laboratory Tests
A debris of the toenail may be scraped and collected by the physician. This will either be examined under a microscope or be sent to a laboratory. The test will be able to identify the type of fungi that is infecting the toenail. This test is important because this will confirm the diagnosis of a fungal infection and not of other conditions which also produces the same type of symptoms [1, 2, 4].
Treatment
After confirming the diagnosis, a physician may prescribe an antifungal agent for the patient. Most of the time, an oral medication is given but an antifungal nail polish may also be advised to the patient. Depending on the type of fungus that is identified, the patient may undergo the treatment for several months. Patients should be advised that the treatment may not be able to rid the fungal infection completely and that there is a chance that the toenail fungal infection will return [1, 2].
Home Remedies
There are several home remedy options that can be done in combination with antifungal medications to cure the toenail infection [7].
Apple cider vinegar
Equal parts of water and apple cider vinegar will be used in this method. The infected foot will be soaked for 30 minutes and then dry thoroughly when done. This should be done every day for a few weeks until improvement in the condition of the toenails are seen [7].
Tea tree oil
A few drops of tea tree oil will be combined with a teaspoon of either coconut oil or olive oil. Using a cotton applicator, the mixture will be applied to the infected toenail. After leaving it for 10 minutes, the nail must be gently scrubbed with a tooth brush. This method must be done two or three times daily [7].
White vinegar
The use of white vinegar will not only fight the infection but it will also restore the normal pH of the skin. One part of white vinegar will be mixed with 2 parts of warm water. This will serve as a soak for the infected toenail for around 10- 15 minutes. It should be rinsed off and dried thoroughly after. This should be done twice every day until the fungal infection is gone. If skin irritation occurs, more warm water can be added to the soak and it should be done once a day instead of twice [7].
Pictures
References
- Khan, A., & Kim, S. (2015, October 19). Fungal Nail Infection. Retrieved from Healthline: http://www.healthline.com/health/fungal-nail-infection#Overview1
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015, July 15). Nail fungus. Retrieved from May Clinic: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nail-fungus/basics/definition/con-20019319
- Walker, B. (2007). The Anatomy of Sports Injuries. Berkeley: North Atlantic Books.
- Wilhelmi, B. (2015, January 21). Nail Pathology. Retrieved from Medscape: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1242733-overview
- ICD10 Data. (2015). Tinea unguium. Retrieved from ICD10 Data: http://www.icd10data.com/ICD10CM/Codes/A00-B99/B35-B49/B35-/B35.1
- Min Han, K. (2016, March 8). Fungal Nails. Retrieved from Medicine.Net: http://www.medicinenet.com/fungal_nails/page1.htm
- Top 10 Remedies. (2015). How to Get Rid of Toenail Fungus. Retrieved from Top 10 Remedies: http://www.top10homeremedies.com/how-to/how-to-get-rid-of-toenail-fungus.html
