Stickler Syndrome
What is Stickler syndrome?
Stickler syndrome is a connective tissue disorder and affects multiple organ. The musculo-skeletal system and different sense organs including eyes, ears are most commonly affected organs. The symptoms are not specific for every case. A wide range of symptoms are included in Stickler syndrome and all the symptoms may not prominent for every affected individual. The symptomatic approach individual specific. The distinctive facial features and palate abnormalities are a classic trend of Stickler syndrome.

The genetic abnormality is the cause of progression of Stickler syndrome. Stickler syndrome is non curable, but therapeutic management provides a better outcome. [1,2]
Symptoms
The most common included symptoms are
The affected children are usually having myopia (nearsightedness). Retinal detachments, early cataract development and glaucoma are other eye problems.
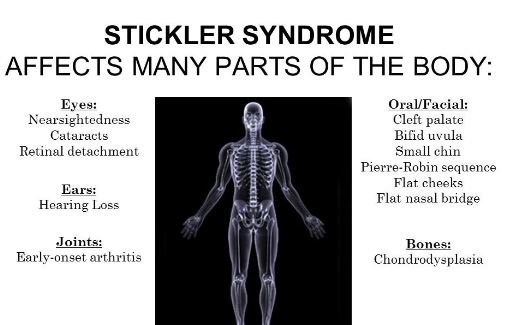
Children having Stickler syndrome are often complaining hearing difficulties. The degree of severity is not same for all affected individuals, but usual finding refers usually individual able to hear loud frequency sound waves. Hearing problems are associated with sensorineural or conductive. Sensorineural hearing problem is associated with altered inner ear and conductive hearing loss may be associated with middle ear abnormality.
Abnormality of Skeletal system includes children affected with Stickler syndrome usually develops flexible joints. Abnormal side curvature in the vertebral column, including scoliosis and flattened vertebrae or platyspondyly cause back pain. In yearly teenage, osteoarthritis also develop.
Some facial deformities including small sized lower jaw, cleft palate or opening in the roof of the mouth, positioned of tongue is in rare side than the normal. These modified facial alterations cause feeding and breathing difficulties of the affected infants. [3,4]
Types & causes
Stickler syndrome is classified into different types depending upon variation of genetic involvement. The symptomatic variations observed in different types are the variability of severity of eye abnormalities and hearing problems.
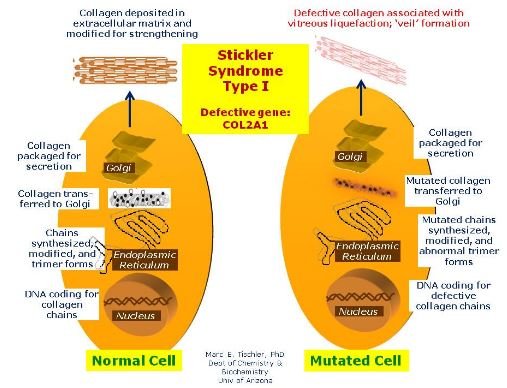
Type I: In this type of Stickler syndrome has the greatest risk of retinal detachment. The cause of type I of Stickler syndrome is mutagenic abnormality in COL2A1 gene on chromosome 12q13.11.
Type II: Eye abnormalities with prominent hearing loss are also common symptoms of type II Stickler syndrome. The cause of type II of Stickler syndrome is a mutagenic abnormality in COL11A1 gene on chromosome 1p21.
Type III: This type of Stickler syndrome is also known as non-ocular Stickler syndrome, as it does not cause Eye abnormalities. But significant hearing loss is noticeable. The cause of type II of Stickler syndrome is a mutagenic abnormality in COL11A2 gene on chromosome 6p21.3.
The most common types of the above mentioned Stickler syndrome are Type II and III.
Rare findings are Types IV, V, and VI, which arise in very few individuals only. [1,4]
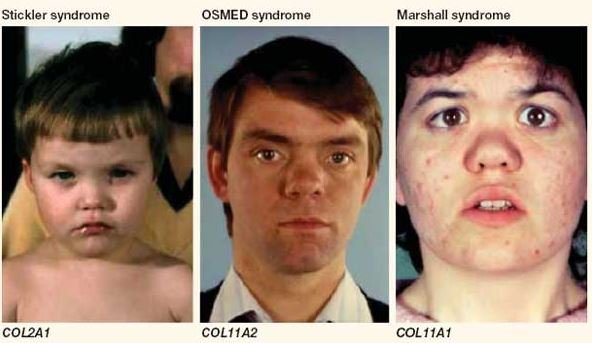
Stickler Vs Marshall syndrome
Both Stickler syndrome and Marshall syndrome have very similar characteristics, including eye abnormalities, hearing loss, distinctive facial appearance and early onset of arthritis. In both the syndrome affected people have short physique.
Type II Stickler syndrome and Marshall syndrome are developed by mutations of COL11A1 gene. Some researchers thought that Marshall syndrome is a type of Stickler syndrome based on these considerable similarities, but this opinion is debatable.
Because the identified individuals have Stickler syndrome type II do not possess distinct mid-facial flattening and better developed nasal bridge in comparison to patients with Marshall syndrome. [1,4]
Diagnosis
Medically based diagnosis of Stickler syndrome involved identification of a gene responsible for this genetic disorders. There are six genes discovered that has a direct link in the development of Stickler syndrome – COL2A1, COL11A1, COL11A2, COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3.
It is also possible that these six gene can mutate with other associated gene and disease progression is possible. But yet now no universal approach for clinical diagnosis is present to detect Stickler syndrome. Clinical evaluation is based upon the following criteria:
- Physical examination
- Patient history
- X-Ray
- Eye examination [2, 4]
Treatment
The goal of the treatment is to control the progression of the symptomatic approach depending upon the type of Stickler syndrome and noticeable in the affected individual.
The treatment of Stickler syndrome requires a team of expert clinicians , including pediatrician, geneticist, ophthalmologist, rheumatologist, orthopedic surgeon, orthodontist, plastic surgeon, otolaryngologist, and other healthcare professionals to prepare patient specific customized treatment plan. Systemic and comprehensively plan are required to treat an affected patient’s treatment.
Some abnormalities, including ocular defects or skeletal malformations need prompt treatment to restrict or delay the related complications and for this early detection of Stickler syndrome is essential. Some restricted life style like avoiding contact sports is advisable for patients with ocular forms of Stickler syndrome due to the risk of retinal detachment. Immediate surgery is required to preserve vision in retinal detachment. But the chance of recurrence of retinal detachment is common even after a successful surgery. In certain cases, some experts advise preventive cryotherapy to reduce the risk of increase retinal detachment.
Cataract surgery, also required to treat the condition and to treat myopia, patients need corrective lenses. Tracheostomy is another surgical intervention, in which respiratory difficulties a tube is positioned at the opening of the neck to prevent respiratory difficulties.
Different craniofacial abnormalities including cleft palate need medical correction of surgical intervention. Dental malalignment (abnormal jaw alignment) correction requires an orthodonture procedure.
Hearing aids are problem solving, supportive treatment for sensorineural or mixed hearing loss and beneficial for certain individuals. A surgical procedure, known as myringotomy, is required small invasion for insertion of small tubes in the eardrum to correct glue ear.
Different anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are prescribed to treat joint problems associated with Stickler syndrome. Corticosteroid injections are also recommended for short-term relief. Orthopedic surgery may require to treat joint abnormalities, including total hip, knee replacement or correction of abnormal curvature of the spine. Physical therapy often recommended for better attaining joint problems.
Different vocational and special education required for children, as they may face learning disabilities due to vision or hearing problems.
Genetic counseling may also require for affected individuals and their families. [2, 3,4]
Life expectancy
Usually in early mortality due to Stickler syndrome is not directly linked with the syndrome, but associated complications can cause death. Otherwise normal life expectancy with Stickler syndrome showed 60 years or more. [2]
References
- Stickler syndrome; Retrieve from: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/stickler-syndrome
- Nathaniel H Robin, Rocio T Moran, and Leena Ala-Kokko, Stickler Syndrome; Initial Posting: June 9, 2000;
- Last Revision: November 26, 2014; Retrieve from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1302/
- Stickler Syndrome, (2014); Mayo Clinic Staff; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stickler-syndrome/basics/definition/con-20027976
- Stickler Syndrome; National Organization for Rare Disorders; ; Retrieve from: http://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/stickler-syndrome/
