Rubella Rash
Define rubella
Rubella is a distinctive rash generative contagious viral infection. Rubella is comparatively less infectious and low complicated health concern in regards of measles.
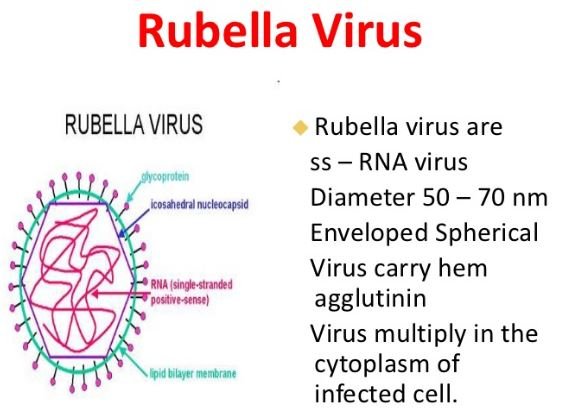
Eradication of Rubella is possible, as effective MMR vaccine is available. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has stated that the United States is free from rubella due to effective immunization program with MMR. (1,2)
Alternative names:
Rubella has following alternative names:
- German Measles
- Three-day measles (1)
Symptoms of Rubella
Rubella usually a mild infectious in nature, so in some cases it may be asymptomatic. The following are the observed symptoms, which can stay only for three days and rid off by their own way:
- Little increase of body temperature (mild fever), that may stick within 1020F
- Headache
- Runny nose or stuffy nose
- Swelling in the eye
- Reddish coloration in the eye
- Inflammation occurs in the Lymph gland present behind the ears
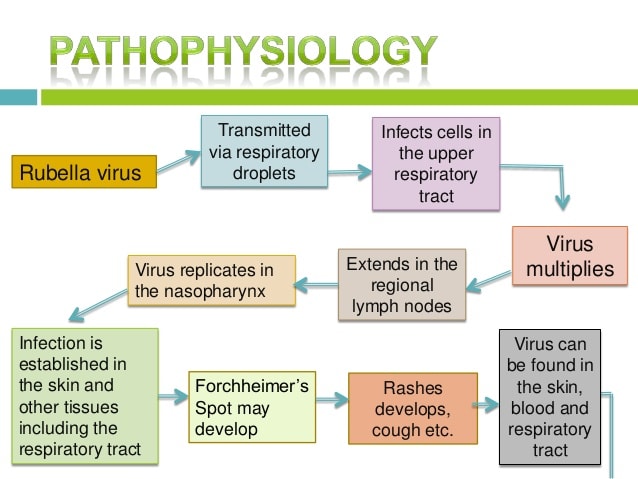
- Reddish pink rashes spread throughout the body. Initially the rash occurs in the face, and gradually extends to the chest, upper limbs and then lower limbs and in the same fashion they disappear in their own way.
- Particularly, young girls usually complaining joint ache. (2, 3)
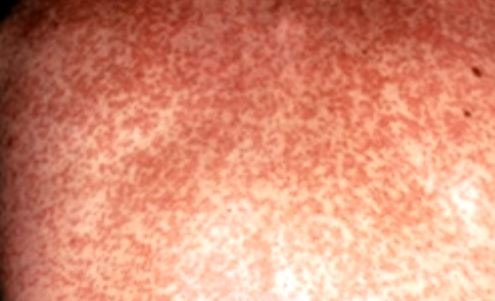
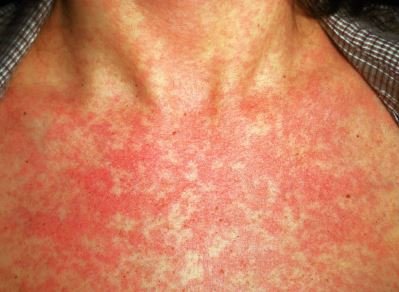
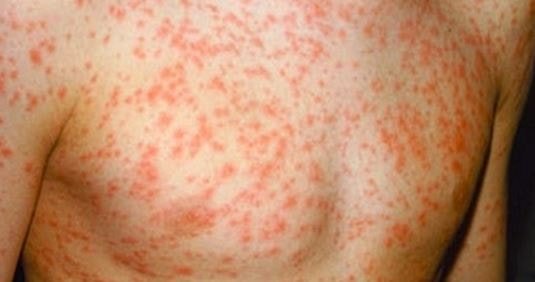
Incubation period
After invading the infectious agent into the host body, a certain period of time gap is maintained to onset of symptoms. During this period, infectious agents grow for further spreading of infection.
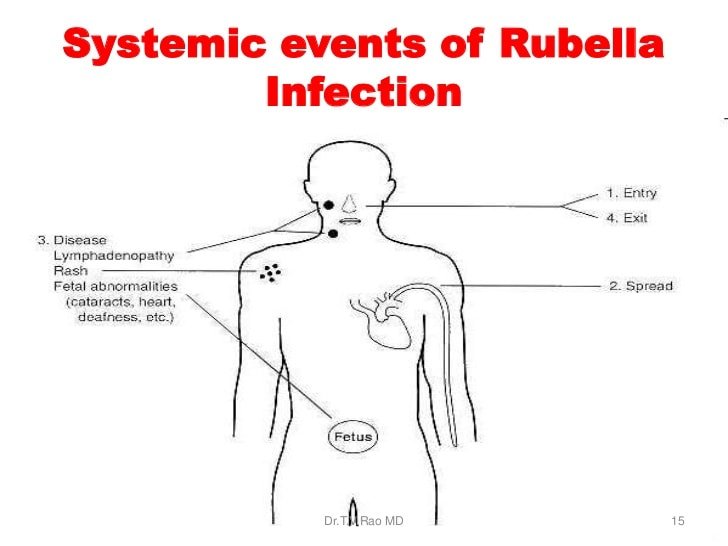
This period is termed as the incubation period. Incubation period for rubella lies within 16 to 21 days. During this period may symptoms are not observable, but the infected person acts as a carrier and can spread the infection. (4)
When need immediate medical help?
Newborn and children are more susceptible in Rubella, it is advisable that if any symptoms mentioned above developments in child, better to consult a pediatrician for confirmation.
Before family planning, it is necessary to ensure that MMR immunization is enlisted in the received vaccine list. Onset of rubella, during pregnancy can create congenital complications for newborn. (3)
Complications of Rubella
Serious complications are obtained, if the rubella infection occurs during pregnancy. In the first trimester women expose to rubella virus can cause serious congenital defects ,which include cardiac problem, brain disorder, vision disturbance, miscarriage and even death of the fetus is possible. Congenital deafness is a most frequent incidence in rubella infection during pregnancy.
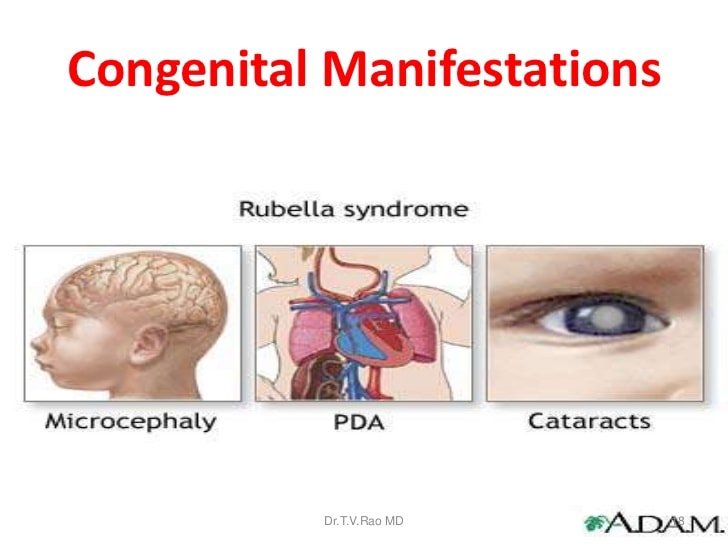
If the infection is affected in between 12 to 20 weeks, then the above mentioned complications become less frequent or milder to the fetus and nearly no risk in regards of the fetus is associated after 20 weeks of onset of infection.
It is highly recommended during pregnancy, women should protect themselves from exposure to rubella virus. Immunization with MMR, is the best option to prevent complications related to rubella. Even though the pregnant woman has already obtained vaccination or rubella occurs after 20 weeks, then also consultation with doctors is must to avoid any future complications. In very rare cases, immunization does not provide protection from rubella.
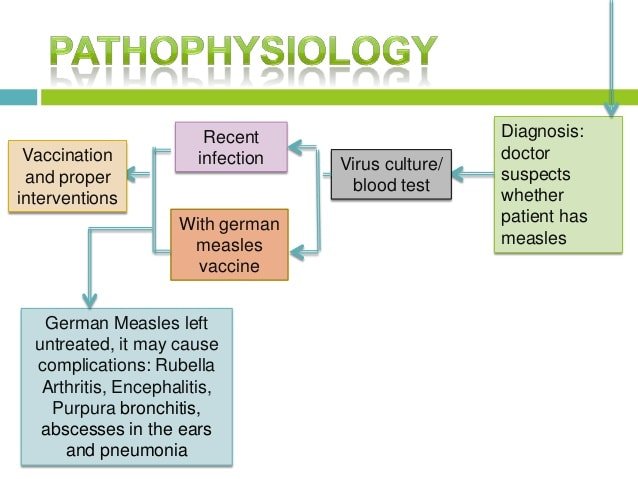
Some other rare complication associated with rubella is joint pain in young girl child or in adults which may even lasts for months. Some children get convulsion during the onset of fever and need immediate medical advice. (1,3,4)
Causes of rubella Infection
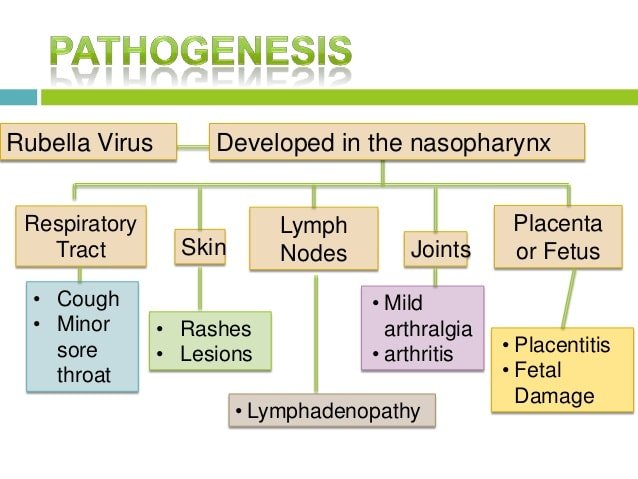
Rubella is a viral infection and rubella itself is the causative agent of the infection and the name came from the same. The rubella is contagious and spread from the infected individual to others.
The mode of transmission is air route. During coughing, sneezing and talking small air droplets are produced and those holding the virus and carry to others.
The other possible indirect transmissions include, unwashed hand, unclean surface, fomites and nose or throat discharges. (3)
Diagnosis
Symptomatic diagnosis is clinically unreliable, as the similar type of symptoms are associated with other viral infections (like measles) also.
A blood test or blood culture is conducted to confirm the presence of rubella. By the presence of rubella antibodies in the blood sample indicates recent exposure to rubella virus or immunization with rubella. (1,4)
Treatment
For symptomatic relief, doctors may advise to take paracetamol or ibuprofen for fever and headache or joint ache. It is also suggested that adequate rest in the home is important, as body become weak and this also prevents spreading of infection to others. Yet know no antiviral treatment is available for rubella. The symptoms are naturally way out within 3 to 5 days after the onset of infection.
Immunization is an important step to prevent and eradicate the Rubella.(1,2,3,4,5)
Fact sheet of Rubella Immunization
- MMR (Mumps, Measles and Rubella) is the vaccine, which safe and effective against the included name of viruses.
- The recommended dose for children is two times vaccinated with MMR, the first dose is administered at the age between 12- 15 months of a child and the second dose is provided at the age between 4-6 years of the child.
- It is essential to check the immunization list, which already incorporated to pregnant women at the very beginning.
- It is now observed that almost 79% of rubella cases belongs to people who have more than 15 years of age. (5,6)
References:
- Mayo Clinic Staff (2015); Rubella; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rubella/basics/treatment/con-20020067
- Rubella – symptoms (2015); http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rubella/Pages/Symptoms.aspx
- Debra Sullivan, (2016); German Measles (Rubella); Retrieve from: http://www.healthline.com/health/rubella
- Rubella (German measles) – including symptoms, treatment and prevention; Retrieve from: http://www.sahealth.sa.gov.au/wps/wcm/connect/public+content/sa+health+internet/health+topics/health+conditions+prevention+and+treatment/infectious+diseases/rubella
- Rubella (German measles); Retrieve from: http://www.cyh.com/HealthTopics/HealthTopicDetails.aspx?p=114&np=303&id=1821
- Facts about Rubella for Adults (2012); Retrieve from: http://www.adultvaccination.org/vpd/rubella/facts.html
