German Measles
What is german measles?
German measles is a viral contagious infection. The infectious agent mainly affects skin and lymph nodes. The onset of german measles can be possible at any age, but younger children are more susceptible, but vaccination can prevent this infection successfully.
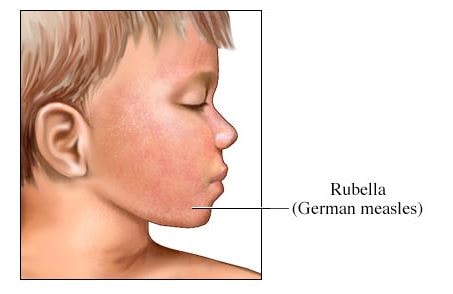
The causative virus name is Rubella, so the alternative name of german measles also termed as same i.e.’ Rubella’. Depending upon the duration of infection and observable symptoms, it is also termed as 3-day measles. (1,2)
Symptoms
The initial symptoms after the onset of infection is mild fever, which can stay for 1 to 2 days. During a fever, the body temperature raises up to 99-100°F.
The gradual symptomatic development provides inflammation and tenderness in the lymph nodes present behind the ear or the backside of the neck.
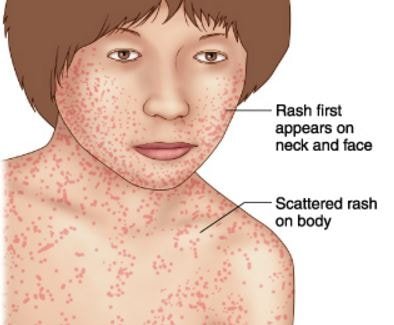
In later stages, prominent rash occurs in the face and gradually covers all over the body. The rash is quite similar with other infectious viral rashes. They are reddish pink in color. The rash usually ends after 3 days and then affected skin may covers with fine scales. The occurrence of the rash is the major sign of the German measles.
Other associated symptoms include:
- Headache
- Anorexia (Loss of appetite),
- Mild swelling in the eye, specifically at the lining of the eyelids and pupil ( conjunctivitis)
- Stiffness in the nose, or sometimes runny nose,
- Other lymph nodes become Inflamed and tendered
- Painful joints in young females
- Almost 50% of the total cases, rubella is asymptomatic. (1,2,3)
Causes
The contagious period is started 10 days before the onset of the rash and it can extend up to 7- 15 days after the rash departs. Therefore, infectious agent can transmit before the symptom (rash) arises.
The causative organism of German measles i.e. Rubella can transmit via the respiratory route. Generally during coughing, sneezing and even talking droplets are produced. This droplets can float on air and intake of air for respiration, these droplets are enter into the body and spread the infection.
The Rubella virus can transmit via mucous secretion from the nose and throat.
Pregnant women can pass on the infectious agent to fetus through blood circulation.
In the present century, the onset of German measles at an early age is almost controlled with the help of vaccination. But it appears mostly in unvaccinated adults, as underdeveloped countries still prevalent in German measles. (1, 6)
Incubation Periods
The average incubation period for Rubella is sixteen to eighteen days, it may vary from 14 to 23 days. Therefore, after exposure to a Rubella virus, there is a possibility of the onset of initial symptom occurrence in between two to three weeks. (6,7)
German measles Vs Measles
The term German measles and Measles may sound similar to a lay person, but clinically they have lots of difference.
|
German measles |
Measles |
| The responsible virus is Rubella | The responsible virus is Rubeola |
| Milder disease | Cause serious illness |
| Lasts around 3 days | Lasts for several days and may associate with permanent damage |
| German measles have pink or light red spotted rash, specifically started from face | In measles whole body cover with red or reddish-brown rash |
| Initial symptoms are mild fever with swollen lymph nodes present behind the neck. | Initial symptoms are high fever, hacking cough, and runny nose |
| Facial rash in the key sign of German measles. | Koplik spots present inside the mouth is the prime sign of the measles. |
| Usually not cause serious health issues | It causes serious health issues. |
Diagnosis
The rash is a common symptom of German measles and other viral infections, therefore after physical examinations and discussion of symptoms, doctors may order a blood test for confirmation.
Blood test helps to identify the presence of rebella antibodies in blood sample. Antibodies are defensive mechanism, produced after any foreign body enters into the body. The presence of specific antibody for Rubella indicates that the virus enters your body or not.
This blood test also helps to judge the effectiveness of the Rubella immunization. (5, 6)
Treatment
Usually no treatment is required to treat German measles, as the duration of illness last for a few days (3 days) and symptoms are mild. But German measles is a contagious infection, so better to keep isolated to prevent the spreading of the infection to others.
This viral infection may cause weakness, so better to take rest in room for one to two weeks and during this incubation period is also over, therefore the chances of spreading the infection become less.
Doctors may prescribe paracetamol or ibuprofen for controlling fever and associated malaise and headache etc.
Immunization is a better option to prevent the infection, specifically for girls, as German measles during pregnancy cause complications. It is advisable that before puberty immunization is must. (6,7)
Immunization/ Vaccine
To eradicate German Measles, every child should vaccinate with MMR (Mumps, Measles and Rubella) vaccine. The recommended dose for children is two times vaccinated with MMR.
- Initial dose is given to 12- 15 months of a child
- The second dose is provided at the 4-6years of age of the child.
If anyone does not immunize with MMR vaccine in childhood and not got measles infection previously, then you should take an MMR vaccine initial dose and second dose should be taken after 28 days of initial dosing.
If anybody once get German measles, then the body becomes immune to the infection and there is no chance to get again infected with the same, so need not to take vaccination against German Measles. (3)
Complications
Rubella virus can cross the placental barrier, therefore if pregnant women get affected with German measles can origin of congenital rubella infection in the newborn. This inborn infection has potential hazardous health issues for the infants.
The possible complications with congenital rubella infection in developing children are who are growth retardation; cognitive disability; cardiac and ocular defects; deafness; and disorder in liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
Arthritis like symptoms include stiffness of the knee, finger and wrist joints. Rarely German measles can cause otitis (ear infection) and encephalitis (brain infection). (3)
Pictures
References
- Rubella(German Measles); Kidshealth; Retrieve from: http://kidshealth.org/en/parents/german-measles.html#
- Rubella(German Measles, Three- day Measles) (2014); Center for Disease Control and Prevent; Retrieve from: http://www.cdc.gov/rubella/about/index.html
- Mayoclinic staffs (2015), Rubella; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rubella/basics/complications/con-20020067
- Michele Blacksberg; The Difference Between Rubella and Rubeola; Retrieve from: http://www.empowher.com/measles/content/difference-between-rubella-and-rubeola?page=0,1
- Rubella (2015); Retrieve from: http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rubella/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Rubella(German Measles); (2015); Retrieve from: http://patient.info/health/rubella-german-measles-leaflet
- German measles (rubella); (2014); Retrieve from: http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/conditions/infections/a5549/german-measles-rubella/
