Pyogenic Granuloma
What is Pyogenic Granuloma?
Pyogenic granuloma also referred to as lobular capillary hemangioma, is a common skin growth that is usually red in color. It is a tiny red bleeding mass that protrudes like some raw meat and may have a rough surface especially if it bleeds a lot.
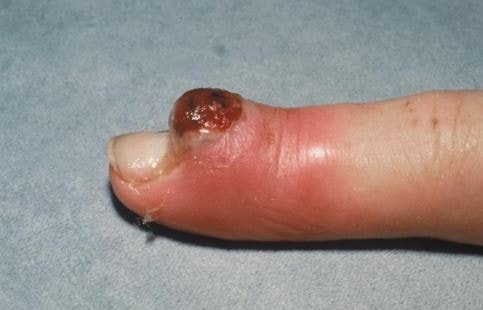
These bumps tend to bleed because of the large amount of blood vessels contained in it and can also spread through local blood vessels. Sometimes a minor lesion will appear and swells fast to a size of a half an inch in just a couple of weeks. Pyogenic granuloma usually occurs on the hands, face, feet, neck, upper trunk, head, and gums in pregnant women.
This skin growth may affect both males and females but are most common in young adults, people who take certain drugs or oral contraceptives, children, and women who are pregnant when there is a change in their hormones during pregnancy which will cause the bumps to develop. Pyogenic granulomas are non-cancerous but although the chance is little, they can also be cancerous.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Pyogenic Granuloma?
A wound commonly appear as a tiny red pinhead-sized, blue-black, or a brownish red in color that can grow up to 2cm in diameter within a number of days or weeks. Every so often the bumps reach up to 5cm.
The sores simply bleed so easily and can form into crusted sores. In general, only one lesion is present but infrequently develops into multiple lesions as well. It appears to be painless according to people who had the condition but their only complaint is the repeated bleeding from the lesion.
What can be the Cause of Pyogenic Granuloma?
The causes of pyogenic granuloma is still not known but there are some factors established that can be the possible cause of the development. These are:
- The infection of virus in the body can be a cause but is still not proven yet
- Developed during a trauma like the sight of a fresh minor injury
- Primary malformations of the microscopic blood vessel
- Staphylococcus aureus is an infection causative organism that is usually present in the lesion
- Lesions triggered by drugs
- Hormonal influences that happens to pregnant women
What are the Treatments of Pyogenic Granuloma?
Treatments depend on the cause of the pyogenic granuloma or the size of the bump itself. If the pyogenic granulomas are small, no treatment is required since these usually goes away on its own. If the pyogenic granulomas are larger in size, the physician will have to remove it.
For pregnant women, the physician will first propose to the patient to wait after delivery in order to see whether the growths disappear or not. If drugs are the main cause of the growths, the patient should just stop the intake of the drugs with the physician being informed, so the growths will most-likely die out as well.
Since the pyogenic granulomas may be cancerous, a sample of this is acquired for biopsy analysis since many of bumps from the treated cases grows back and requires another treatment. The type of bump that pops up on the upper back usually comes back and sometimes, not just one occurs but small multiple granulomas.
If not treated right, pyogenic granuloma can grow back even after removal or if the growths are not removed completely, the remains may spread to the blood vessels in the exact area.
Pictures
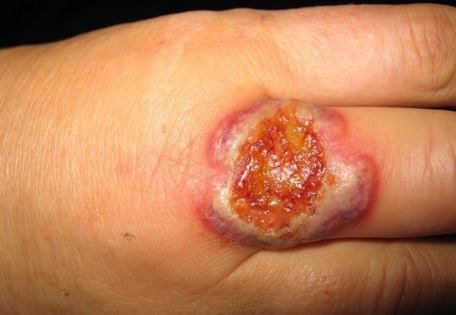
Image 2 – pyogenic granuloma on back of finger
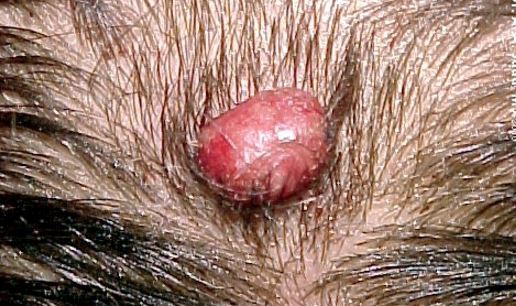
Image 3 – pyogenic granuloma over scalp
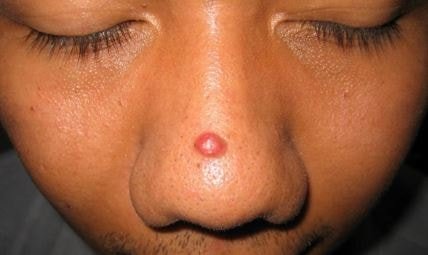
Image 4 – pyogenic granuloma over nose
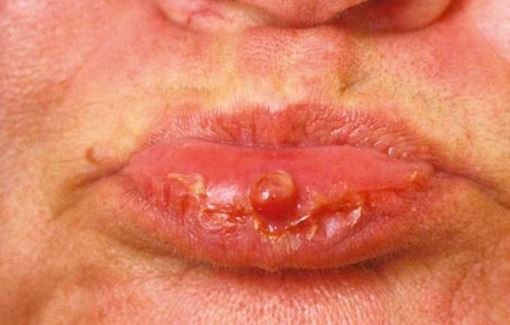
Image 5 – pyogenic granuloma over tongue
How is Pyogenic Granuloma Removed?
Pyogenic granulomas are removed when it is already big. Below are some ways to remove the growths:
- With the use of curette, the physician will scrape off the pyogenic granulomas and cauterizing it to stop the growths from bleeding and for it to lessen the chance to recur but an anesthesia is needed for this type of procedure
- Imiquimod application wherein the immune system is triggered to release chemicals to fight off and destroy cancer cells and viruses in the body
- Cryotherapy is used to freeze up small lesions
- Chemicals like silver nitrate or podophyllin are also used by some physicians for the bleeding
- Laser surgery can be done to shrink or remove lesions but it is not widely proven to be very effective or superior
- The most effective surgery that is more effective than just scraping it off with the largest amount of cure rates is by removing the entire growth by surgical excision and stitching it afterwards to close the lesion
- Pyogenic granulomas can also grow on the eye and it can be removed through surgery or ointments with corticosteroids to minimize the inflammation.
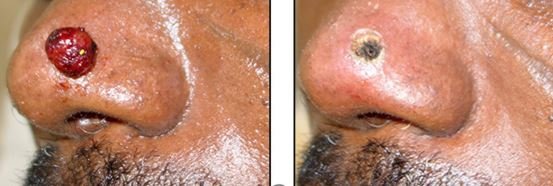
Image 6 – Before and after surgical removal
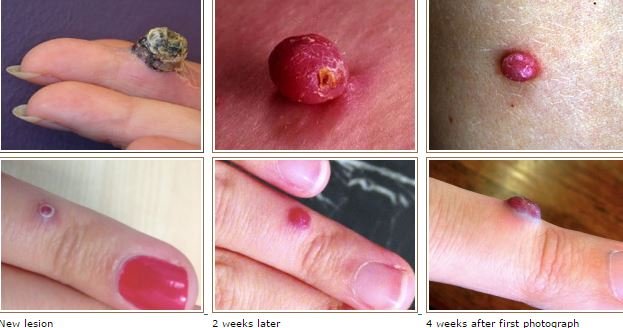
Image 7 source from http://www.dermnetnz.org/
References
- Overview, Location, Causes, Complications, Diagnosis, Treatment at http://www.healthline.com/health/pyogenic-granuloma#Description2
- What treatment is available for pyogenic granuloma? How is pyogenic granuloma diagnosed? at http://www.dermnetnz.org/vascular/pyogenic-granuloma.html
- Pyogenic granuloma: American Osteopathic College of Dermatology (AOCD) http://www.aocd.org/?page=PyogenicGranuloma
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G. et al. (2006). Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
