Marsupialization
Marsupialization is a surgical procedure that is a treatment option for the development of Bartholin gland cyst. This operation is advised to women whose glands have large abscess which makes excision of the gland not a viable option [1, 2].
Anatomy and Pathophysiology
The Bartholin glands, also known as greater vestibular glands, are 2- 0.5 cm diameter organs which are found on either sides of the labia majora. They are normally unpalpable unless they afflicted with a pathologic condition. These glands produce mucus which they release through their ducts. These ducts open into the sides of the vaginal orifice and ensure that the vestibular surface of the vaginal mucosa is continuously moisturized [1, 3].
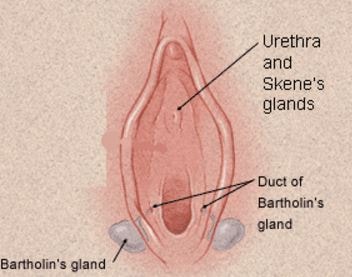
Figure 1 shows the location of the Bartholin glands.
The most common pathologic conditions of the Bartholin glands are cysts and abscess formation. When the openings of the Bartholin gland ducts become obstructed, the mucus can’t be released into the vagina and buildup into the ducts. The Bartholin glands may grow up to 1-3 cm and may become palpable. This condition may not produce other symptoms aside from the enlargement of the glands. The glands may further increase in size following a sexual activity because they are stimulated into producing more mucus. If the accumulation of mucus gets infected, it will cause an abscess of the Bartholin glands and may produce symptoms such as redness and swelling of the glands [1, 3].
Excision of the cyst and drainage of the abscess may be enough to treat the condition, but if the abscess formation is reoccurring, the physician may recommend doing a marsupialization [3, 4].
Marsupialization
Indications and contraindications
This surgical is recommended for women whose Bartholin gland cyst failed to respond to other mode of treatments and those who have a history of reoccurring cysts. It is also advised for those who experience pain and discomfort due to these cysts. The main contraindication for this procedure is the patient’s refusal to undergo the procedure [1, 2].
Anesthesia
The anesthetic agent that will be used for this procedure can be a local anesthesia, a procedure anesthesia or a combination of both. A local anesthetic agent, such as mepivacaine and lidocaine, should be given in order to reduce the discomfort felt by the patient after the procedure. The use of epinephrine may also be beneficial because of its vasoconstrictive capabilities in order to minimize bleeding which can cloud the surgical field [1, 2].
Position
Patient will be placed in a lithotomy position. Stirrups such as Allen, Candy Cane and Yellow fin may be used to ensure proper positioning of the patient. Maintaining a proper position will not only be beneficial during the procedure but it will also prevent any unwanted injury to the patient [1, 2].
Technique
The extent of the abscess or the cyst is identified through a bimanual examination. The labia will be retracted in order to expose the introitus of the vagina. The physician will make an incision over the vaginal mucosa from the introitus and down to the wall of the enlarged Bartholin gland. The wall is continuously incised until a substantial amount of the gland is exposed. If there is abscess, the content of this will be evacuated. Sample of this abscess will be submitted for a culture test. After the draining the contents of the cyst, the wall of the gland will be sutured laterally to the introitus skin and medially to the vaginal mucosa [1, 3].
Complications
Possible complications of a marsupialization procedure may include postoperative infection, continued pain, recurrence and scarring. Neuropathy of the operated area may also happen but it rarely does [1].
Postoperative Care
Medications
Oral pain medications may be taken by the patient after the effects of the anesthesia have worn off. Common medications that may be prescribed are acetaminophen and Ibuprofen. If the pain that the patient is experiencing is severe, a narcotic agent may be prescribed by the physician [1].
Antibiotic agents are not normally given to patients unless there is abscess or a sign of cellulitis. The agent that will be prescribed will depend on the result of the culture test that was performed. It is important to remind the patient to complete the entire course of antibiotic treatment [1, 2, 3].
Incision care
The physician will advise the patient on when the wound dressing may be removed. After this, the area should be washed with warm, soapy water every day and kept dry. A gauze may be used to cover the wound and prevent it from rubbing against clothing. Sitting in a hot sitz bath for 15-20 minutes for 3 times a day will help hasten the healing process [1, 5].
Recovery
Patients should be informed that it would take around 2-4 weeks for the wound to completely heal and any sexual activity should only resume 4 weeks after the procedure. During the recovery time, wearing tight clothes should be avoided and cotton underwear must be worn instead [1, 5].
References
- Perry, T. (2015, November 15). Bartholin Gland Marsupialization. Retrieved from eMedicine: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1894499-overview
- Wheeless, C. J., & Roenneburg, M. (2015). Bartholin’s Gland Cyst Marsupialization. Retrieved from Atlas of Pelvic Surgery: http://www.atlasofpelvicsurgery.com/1VulvaandIntroitus/3bartholinsglandcyst/chap1sec3.html
- Quinn, A. (2015, September 10). Bartholin Gland Diseases. Retrieved from eMedicine: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/777112-overview
- Wint, C., & Solan, M. (2015, September 25). Bartholin’s Abscess. Retrieved from Healthline: http://www.healthline.com/health/bartholins-abscess#Overview1
- Healthwise Staff. (2015, May 15). Bartholin Cyst Surgery: What to Expect at Home. Retrieved from MyHealth.Albert.Ca: https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=zy1271
