Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic disorder which affects the skeletal muscles. This is one of the major types of muscular dystrophy in which muscular tissue become degenerated and loses their intactness which makes them weak. The severity is high in comparison to other muscular dystrophy. The proximal muscle is mainly affected which attach at the neck, shoulder and hip joints.
The fine movement of the body is less affected, such as it does not interrupt the finger movement, hand movement. It hampers walking or other major movement of the body. The symptoms are progressive, though at the time of birth, it is not noticeable. The onset of symptoms is usually within the age of 3 to 5 years. During the first onset, the disease progression rate is slow. By increasing the age the quick rate of disease progression occur. The incidence rate is high in boy child, it rarely affects girls.
Symptoms
- The major symptom of this disease is muscle weakness. At the early childhood (3years), the shoulder muscle, thigh muscle, hip muscle, pelvic region and thigh become start to degenerate and gradual weakness developed.
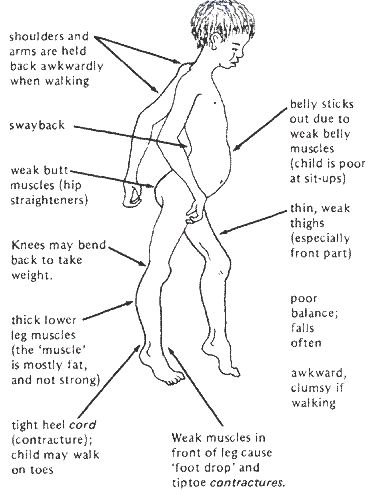
Image 1 – Symptoms of DMD
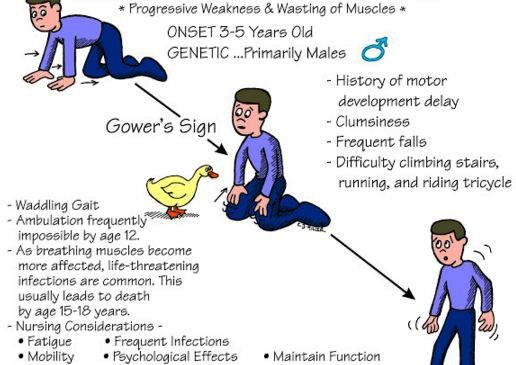
Image 2- Gowers Sign in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- The calf muscle of the leg is enlarged at the initial stage. This enlargement is termed as ‘false enlargement’ or ‘pseudo enlargement’; this occurs due to deposition of the degenerated tissue.
- Gradually muscles of the hand, legs, and trunks of the body get affected.
- Children are late walker than the normal child.
- At the early age, the children are mostly walking on their toes and easily fall down.
- The typical posture followed by the affected child for getting up after fall down. They first keep their hand on their knees and then lift up the posterior part of the body. Then they provide pressure in their hand to move up the upper part of the body.
- Difficulty is observed in raising the hand of the child.
- During the age of 7-9 years child require to wheelchair to cover long distance and gradually with increasing their age, the walking difficulties increase and they totally depends on wheelchair.
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy has no pain symptoms, some patient may complain about the muscle cramp, which can be managed by analgesics.
- Sensation related problems are not arises, as nerves are not become affected.
- Heart muscle becomes weak and this can be a life threatening for patient. This is occurring at the adolescent age.
- Respiratory muscle include diaphragm is become weak and hamper the respiration. Lungs become incapacitate to inhale or exhale air properly which leads to shortness of breathing. This symptoms are mainly arises after 10 years of age and may child not understand the shortness of breath, but associated symptoms are also very prominent which include headache, difficulty in concentrating, sleep disturbance.
- Mental development is not adequate as compare to normal child. Usually most of the children are facing learning difficulties due to mental dullness. Some Children can develop mental retardation.
Genetics
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a disease due faulty gene function. The DNA present at the gene produce different types of protein, one of the important proteins synthesized by DNA is ‘dystrophin’ which help to keep muscle fibers intact. Absence of this protein cases, loss of strength of the muscle.
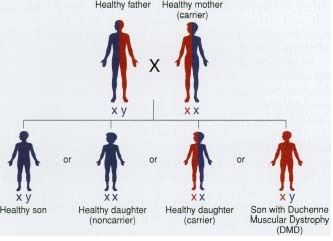
Image 3: Genetic overview of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy
This faulty genetic structure may or may not transfer from parents. In usual cases, the child carries one pair of gene from father and other pair of gene from the mother. The mutation of these genes forms the child’s genetic structure. Boy child having one X chromosome and one Y chromosome and girls is having both X chromosomes.
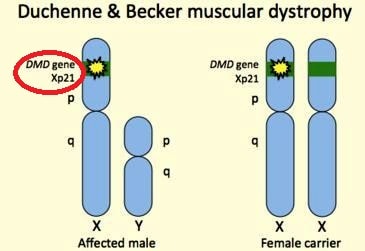
Image 4 – DMD gene xp21
It has found that X-linked chromosomes get affected in case of inherited DMD. For girl child, both chromosomes are X and in case of mother carry the faulty gene, then one faulty chromosome can compensate other and rarely girl child become affected. Whereas boy child has one X and another one Y and they cannot compensate each other and mostly get affected.
If the mother carries the faulty gene, then there is a 50% chance of development of the DMD in her boy child and 50% chance that her girl child can carry the faulty gene.
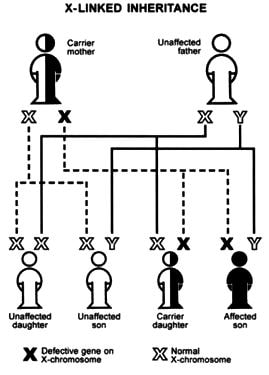
Image 5
DMD can also form, during the faulty mutation of the child’s gene formation stage.
Treatment
DMD is an incurable disease. The following treatment is given to reduce the progression of disease or for controling the symptoms.
- For reduction of the disease progression steroidal drugs are prescribed.
- For control the asthma exacerbation Albuterol is used.
- Different cardiovascular drugs are prescribed to control the cardiac problems which include ACE-inhibitor, Beta blockers and diuretics etc.
- Orthopedic aids, including wheel chair, braces are used for patient mobility.
- Physical therapy helps to keep muscles active
- Ventilation may require with advancing the disease, as the lungs are not functioning properly.
- Novel treatment approaches are gene therapy and stem cell therapy. Researchers are still working on this approach and hope in future DMD will be curable.
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients is in between 25 -30 years of age. Mostly death occurs due to lung disorders.
DMD Pictures
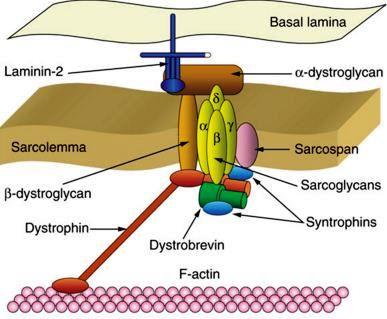
Image 6 – DMD Pathophysiology
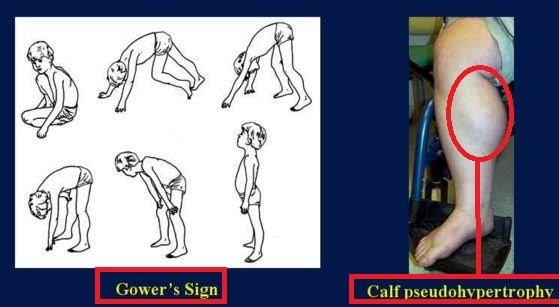
Image 7 – Gowers Sign and Calf Pseudohypertrophy (degenerated muscle deposition)
References
- https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000705.htm
- https://www.mda.org/disease/duchenne-muscular-dystrophy/overview
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/muscular-dystrophy/basics/symptoms/con-20021240
- http://patient.info/health/duchenne-muscular-dystrophy-leaflet
- http://www.cureduchenne.org/about-duchenne.html?referrer=https://www.google.co.in/
