Herpangina
What is herpangina?
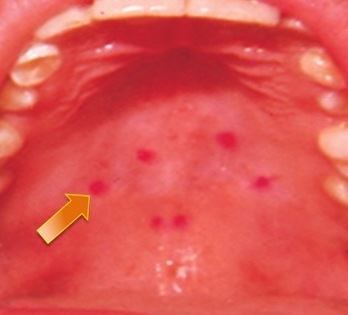
Harpangina is an example of viral infection. Usually the infectious virus affects young age child during summer season. The characteristic of the herpangina includes blister like sore or ulcer developed on the palate (roof) of the mouth.
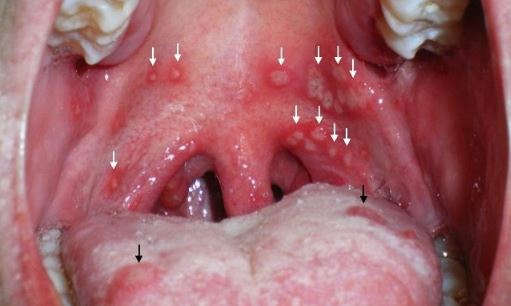
This is a contagious disease and caused by enteroviruses. The virus is easily contaminated from one child to another child, as the virus is transmitted via unclean hand, germ-infected floor, and droplets formed during talking, coughing or sneezing. (1,2,3)
Symptoms
After entering the responsible virus into the bloodstream, the incubation period is started, which may last for 1 to 2 weeks and infected patient may asymptomatic during this period.
- After completion of the incubation period of the virus, the infected child has sudden onset of high fever with sore throat. The body temperature can increase up to 1060F during fever and difficult to lower down the temperature at a normal level.
- Infected child is complaining of headache and throat pain.
- Affected child has inflamed lymph gland and creates difficulty in swallowing.
- Child does not want to eat or drink due to pain in the throat and onset of anorexia is common.
- Ulcer becomes prominent at the palate of the mouth about two days after the initial infection.
- The ulcer has a distinct reddish border with garish white color.
- The blister shaped ulcers are painful and occur varying in number.
Situation need immediate medical attention
- Body temperature increase up to 1060F for more than an hour.
- The ulcer remain in the mouth for prolonged periods (more than 5 days)
- Dehydration symptoms, which include dry mouth, inadequate tear, tiredness, decreased urine volume, urine coloration becomes dark and sunken eyes.
- Commencement of rash (3,4)
Causes
The different strains of enterovirus are responsible for the onset of herpangina. The commonly obtainable or identified strains of enterovirus are coxsackievirus A16, enterovirus 71, and coxsackievirus B. In rare cases the involved enteroviruse strains are parechovirus 1, echovirus, adenovirus, and herpes simplex virus (HSV).
All the included Enteroviruses 71 are belong to the Picornaviridae family. The specific Enterovirus 71 responsible for the development of the herpangina differs with other types of Enteroviruses 71, which can cause encephalitis, myocarditis, poliomyelitis-like paralysis, aseptic meningitis, and neonatal sepsis.
The chance of myoclonic jerks is probably associated with post-infectious neurologic sequelae and usually attack may appear more than 4 times at every night .
If the herpangina develops during pregnancy, then the risk of complications include low birth weight, premature deliverance, and SGA (small-for-gestational-age) means development of an infant has been insufficient or low at every gestational age, respectively. (1,2,3)
Does Herpangiana is Contagious?
Herpangina is a contagious disease and the transmission mode of Enteroviruse that causes herpangina is typically conducted by the fecal-oral route. Another possible mode of transmission includes the respiratory route or via fomites.
The reservoirs of the infectious agents may be fresh water sources like lakes, where viruses can grow, as the moist environment provide a favorable environment for growth of the Enteroviruses.
Other than this, the responsible virus can be alive on exterior and objects, such as toys and countertops for quite a lot of days.
After infectious agents enter into the physiological system and infect the affected individual, the symptoms do not arise immediately, as herpangina usually has an incubation period of 4-14 days. After this certain period of time, the infection causative viruses find in the blood stream. During incubation period, the virus is mostly spread to other individuals. (3,4)
Who is at risk?
Mostly the children below 5 years of age are very much susceptible towards herpangina at summer or during fall season. The children are mostly affected when they are in a group like in school, camps, playground, childcare centers, etc. as herpangina is a contagious disease and easily spread via contaminated surfaces, unhygienic hands or during sneezing and coughing. (3)
Diagnosis
Herpangina is diagnosed by physical examination of the ulcers and discussion of symptoms occur and knowing about the medical history of the individual. In rare cases, special laboratory tests are ordered, which include:
- Sample collected from the nose or throat is examined for identification of the virus. Usually the symptoms are eliminated between the time of test reports obtain.
- The estimation of antibodies to coxsackievirus may also perform. (1,3)
Treatment
The aim of the treatment of herpangina is to provide symptomatic relief, as this infection is self limiting and the virus cannot eradicate by treating with antibiotics, unless doctors uncover some associated bacterial infections. The symptoms usually disappear after one week and doctors prescribe medication depending upon the age, severity, tolerance, other medical history like drug sensitivity. The usual treatment measures prescribed for treating the herpangina are as follows:
- Oral NSAIDs like acetaminophen or ibuprofen is preferable choice for reduction the pain and subside the fever.
- Dietary measures can help to reduce the discomfort like intake of cold milk, ice-cream, blunt foods, as these can reduce the discomfort and do not create any throat irritation. The avoidance of irritable food items like hot spicy foods, citrus fruits or fruit juice can also reduce the discomfort.
- Application of topical anesthetics, including xylocaine or benzocaine in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is helpful to control the pain and discomfort. (1,2,3)
Prevention
Any type of infection can be prevented by maintaining the proper hygiene and this is also applicable for the herpangina prevention.
- Hand hygiene is very important to prevent the spreading of the herpangina. Thorough hand wash before eating and after playing or using the toilet is very important measure for prevention of herpangina.
- Always cover the face during sneezing or coughing
- Keep away from soiled diapers
- Regular clean all the toys for your children and other usable items
- Routinely clean floor surface, toilet, bathroom with germicides.
- Do not send Infected child to school or any group activities and should be isolated by from other children to prevent the spreading of infection. (2)
Pictures
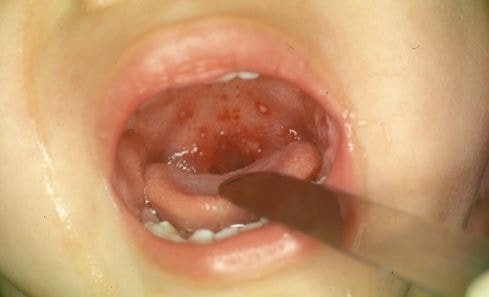
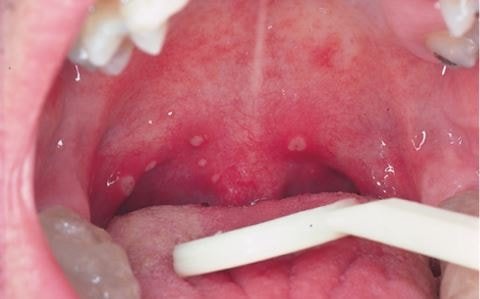
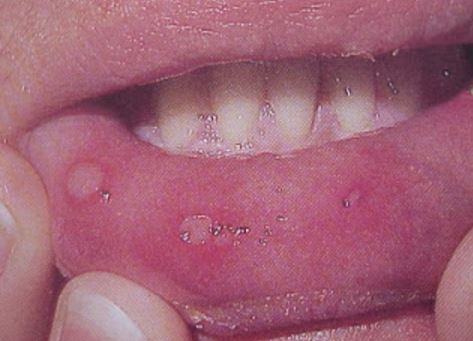
References
- Neil K. Kaneshiro (2015); Herpangina; Retrieve from: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000969.htm
- Sandra G Gompf, (2015); Herpangina; Retrieve from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/218502-overview#a4
- Ann Pietrangelo (2016); Herpangina; Retrieve from: http://www.healthline.com/health/herpangina
- David Perlstein (2015); Herpangina; Retrieve from: http://www.medicinenet.com/herpangina/article.htm
