Spotting Between Periods
What is Spotting between Periods?
Spotting in between periods takes place when there is vaginal blood flow in between the period after your last day of menstruation and the beginning of your next menstrual cycle. Spotting between periods is not really an unusual occurrence.
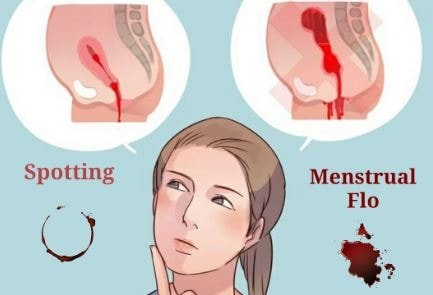
Typically, the menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 days, with an average of 28 days. Vaginal bleeding between periods does not generally pose a major cause for concern, but still warrants attention from the gynecologist. However, there are some cases of spotting between periods that signal a more serious underlying medical condition that would need an immediate intervention.
Bleeding between periods are also known as irregular periods. It means that women do not properly develop and release a mature egg every month as they should normally. Bleeding between periods may also be termed as metrorrhagia.
Spotting between periods may cause different characteristics of spotting such as:
a. Brown Spotting between Period
Brown spotting in between periods means that blood has dried at a certain degree and has been confined to the cervix for a longer period of time. It is most often associated with old endometrial tissues and for whatever reason during your last menses the entire uterine lining failed to make a timely exit. Brown discharge might happen right after periods, and is just “cleaning out” your vagina.
This also may occur when you are ovulating in the middle of menstrual cycle. Spotting is often brownish in hue because it’s less fresh and has oxidized. True spotting consists of blood, however, and should therefore have very little odor. Brown spotting is old blood that has taken a while to come out because there’s not that much of it. Taking birth control pills that do not suit the individual may also lead to brown spotting between periods.
b. Light spotting between periods
Light spotting is known as vaginal bleeding between menstrual cycles. In some cases, the bleeding may be very light and would be noticeable only on the tissue paper after wiping. Most women will experience it in her life at some point or another.
However, in some conditions it can be an indication of underlying reproductive health concern. Light spotting between periods, or abnormal bleeding between periods, can happen for a variety of reasons and it is very common among menstruating women.
Sometimes, spotting between periods may have an easy explanation, like the use of oral contraceptive pills or ovulation. Failure to take the oral contraceptive pill for several days may lead to breakthrough bleeding or spotting because of sudden decrease in estrogen levels.
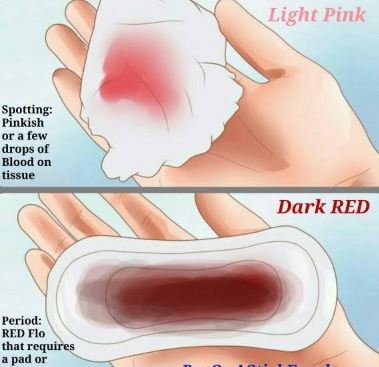
Is Spotting between Periods Normal?
The light spotting between menstrual cycles is fairly normal when conditions are present such as the use of pills. However, in some conditions it can be an indication of underlying reproductive health concern which needs further evaluation by a gynecologist. Spotting between periods should always be treated as something that is not normal in order to have early detection and management.
Causes:
There are a number of causes of spotting between periods, these include:
Abnormal uterine lining or endometriosis
The over proliferation of the inner lining of the uterus or endometriosis results from extension of the endometrial layer into the external cervical os, which when irritated can easily slough off resulting in spotting.
Pregnancy
Mild spotting may be due to the implantation of the embryo in the endometrial layer which sloughs off some portion of it. However, when spotting occurs during the next nine months of pregnancy, it is not considered normal because it may be a sign of a threatened abortion, placenta previa or other problems in the mother and fetus.
Menopause
The fluctuations of hormones in the body such as estrogen and progesterone during menopause cause spotting. Dryness in the vagina as a result of poor lubrication during intercourse may also lead to such.
Cervical or uterine polyps
Presence of polyps in the uterus or cervix may cause rupture of blood vessels in the area causing spotting.
Use of oral contraceptive pills
Failure to take contraceptive pills required for the day changes the hormone levels which results in spotting. Management involves taking the missed pill plus the regular pill for that day.
Cervicitis
Inflammation of the cervix may also lead to spotting
Stress and anxiety
Anxiety and other forms of emotional daily stress, overwork and fatigue can cause irregular periods. If these factors are not controlled, they could make you lose emotional stability. Therefore, these could affect your body functioning balance, producing alterations that will lead to irregular periods. Either way, keep in mind that the physical causes for irregular periods are much more frequent.
Use of Anticoagulants
The use of blood thinners may lead to bleeding because of poor blood clotting. It is important to monitor the clotting time and bleeding time of the patient to prevent bleeding.
Other conditions that may result in spotting between periods include:
- Cancer in the reproductive organs
- Cervical biopsy or any procedure involving trauma to the reproductive organs
- Injury to the vagina as caused by intercourse, polyp, infection, ulcer, varicose veins or genital warts
- Intrauterine device
- Hypothyroidism
Diagnosis
The diagnosis can often be made on the basis of the following:
- Bleeding history
- Physical examination focusing on the reproductive system
- Other medical tests as appropriate such as:
- Pregnancy test
- Hormonal tests
- Pap smear
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- CBC- If bleeding was excessive or prolonged
- Hysteroscopy with biopsy or a dilation and curettage for abnormal endometrium
- The goal of the diagnostic tests is to rule out the underlying cause of the spotting. Biopsy is usually done when signs of malignancy are observed.
Treatment
Usually, women seek treatment in the presence of profuse bleeding. It is important to note that medical consult should be sought at the start of spotting because presence of profuse bleeding may already cause significant blood loss which may lead to complications. Treatment of spotting between periods depends on the cause of the bleeding. The focus of the treatment is eradication of the cause. For dysfunctional bleeding, the ob-gyne may do the following management:
Dilatation and Curettage
Dilatation and curettage involves the insertion of a curette to remove endometrial tissues that is causing the bleeding. The endometrium should only proliferate normally to allow for implantation. Excessive proliferation would need removal of the excess. Women undergoing dilatation and curettage are often sedated. Some portions of the tissues are examined and sent to the laboratory for histologic examination.
Hormonal Replacement Therapy
In cases of menopause or abnormal hormone levels, replacement is the best alternative. Estrogen and progesterone is given to halt the frequent spotting between periods.
Home Management:
If bleeding is very heavy immediately seek consult from a health care provider.
Monitor the number of tampons or pads used in a day to quantify blood loss.
Aspirin use should be properly monitored. Simple aches should be managed by NSAIDS such as ibuprofen to prevent abnormal bleeding.
Complications
Light spotting between periods can lead to the following complications:
Hypovolemia
Prolonged spotting may cause the depletion of blood from the circulation.
Shock
Unmanaged hypovolemia may eventually result to shock as manifested by severe hypotension.
Uterine artery embolization
This is the occlusion of the blood vessels supplying the uterus as a result of blood clots.
Iron deficiency anemia
Prolonged loss of red blood cells may deplete the hemoglobin and RBCs in the body that may result in weakness, easy fatigability and paleness.
Prevention
You can prevent and reduce the occurrence of light spotting between periods by following some of these tips:
- Keeping yourself stress-free since both physical and psychological stress can initiate light spotting between periods
- Managing healthy weight
- Taking suitable birth control pill
- Getting regular tests to check for the growth of any cancerous cells
- Reducing your intake of aspirin since it is a blood thinner and can cause bleeding between menstrual periods
- Maintaining a menstrual diary to help your doctor determine the cause of bleeding between periods.
