RSD Disease
What is RSD disease?
RSD disease has multiple clinical synonyms like complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) or Sudeck atrophy. This condition is associated with vasomotor disorder, inflammation and trophic alterations.
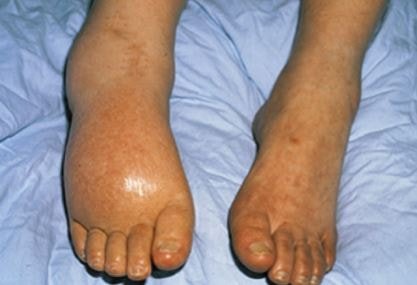
Along with these, some other clinical features may also include like excessive perspiration in palm, armpit, and feet and scalp (hyperhydrosis), enhance the nerve stimulation with increasing pain sensation (allodynia) and alteration of growth of the nails and hairs.
Abnormalities in motor activities such as involuntary movement, tremor and muscular spasm have been reported. The effect of the disease may unilateral or bilateral. This disease condition is considered as a peripheral clinical condition, but it mainly affects limbs and trunks. In case of RSD disease, no underlying neurological injury has been reported.
Symptoms of RSD disease
The included symptoms of RSD disease are as follows, which may occur after six months of the injury.
- Burning sensation associated with pain symptom
- Abnormally high sensitivity towards pain
- Warmth
- Tenderness
- Inflammation
- Edema
- Excessive sweating
- Flushing
- Discolored and shiny skin due to blood circulation is altered in cutaneous tissue
Causes
The actual history of RSD disease development is unclear. The considerable pathophysiological changes in both central nervous system, including substantial nigra and peripheral nervous system, including primary synapse dysfunction may occur.
Other possible patho-physiological changes, including over activity of the sympathetic nerves, response of neurotransmitter is altered. But the level of adrenalin or nor adrenalin and other neurotransmitter in plasma is lower than the normal.
It has also assumed that local abnormal mediators such as vasoactive poly-peptides and substance P release are also responsible for generating the RSD disease. The disease progression and resolution is not same for all the cases. Three stages are recommended for clinical and radio graphical features. According to these features the considerable three stages are as follows:
- Pathophysological changes in stage 1 are characterized as pain development which is associated with inflammation and edema. Evidence of radiology also reported patchy osteological changes also occurs.
- In stage 2, chronic pain with degeneration of cutaneous and bone tissues, joint stiffness are common features. Loss of bone density is found in radiography.
- In stage 3, the patient pain sensation is gradually decreased with some active movement. Passive movement raises the pain sensation. The treatment outcome is less favorable in this stage.
The cause of development of the RSD is varied and most of the cases unknown reason mainly develops RSD disease, other included causes are as follows:
- Minor traumatic injury.
- Sometime the cause is spontaneous mainly in case of immobility intermittent disease may reason behind the RSD development.
- Central nervous system disorders
- Cardiovascular disease including myocardial infraction
The other triggering factors are as follows
- A number of drugs are responsible for the development of RSD, which include phenytoin, phenobarbitone, isoniazid. Other than these immune-suppressants such as tacrolimus and cyclosporine. Even recently reported that rapamycin (immune-suppressive agents) also induced RSD.
- The concurrent medical conditions like diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, type IV hyperlipidaemia and hyperthyroidism are also enhancing the chances of RSD disease development.
Treatment
Early diagnosis of the condition provides a better outcome of the treatment.
- Cold compression or water base ointment massage can relief burning sensation.
- Gentle regular exercise can help to restrict joint stiffness.
- Analgesics are prescribed for pain relief
- In case of severe pain and other worsening symptoms can be controlled by prescribing steroidal drugs like prednisone. When a patient’s condition is controlled, then gradual decreasing of the dose is recommended.
- Amitriptyline, clonidine and pregabalin are the different medications also used for treating the RSD disease.
- Sometime parenteral administration of anaesthetic drugs is also recommended for treatment or diagnostic purpose.
- Surgical sympathectomy is conducted for interrupting the sympathetic over activity.
- Surgical intervention is also conducted for implanting intrathecal drug pumps or spinal cord stimulation device for pain management.
Prognosis
The treatment, prognosis in case of RSD disease is not following the strict outcome. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment provides better results.
Complications
Severe disability occurs due to affected extremities. This is more common in lower limbs. The first indication of this situation is lowering of the temperature in the affected limb. In stage 1 this development of this condition is lower as the temperature of the skin is warm.
References
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/394928-overview
- http://www.medicinenet.com/reflex_sympathetic_dystrophy_syndrome/article.htm
- http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/content/39/7/692.full
- http://radiopaedia.org/articles/complex-regional-pain-syndrome
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9552109
