Outer Ear Infection
What is outer ear infection?
Outer ear infection is the infection, when it spreads from opening of the ear to ear drum. Anatomically, a narrow diameter tube is connected from the outer ear to the ear drum. Therefore, any infection occurs in this tube can affect the whole outer ear.
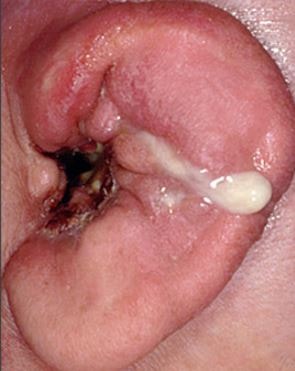
Figure 1 – Outer ear infection (pus discharge)
Clinically, this infection is termed as “otitis externa” and the common people called this infection as “swimmer’s ear.” This infection is frequently developed in youngsters, who are practicing swimming for prolonged periods.
The thin skin lining is covered the ear tube and the lining of the ear gets affected with bacterial or fungal attack in outer ear infection. (1,2)
Symptoms
The symptoms which arise in the outer ear infection are as follows:
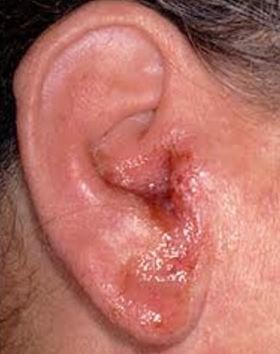
- Inflammation in the ear and in severe case swelling extend to face and behind the neck
- Redness is common at the outer part of the ear
- Warmth
- Pain outer and inside the ear canal
- Difficulty in chewing and even swallowing
- Tingling sound may occur
- Discharge of pus (figure 1)
- Fluid drainage from the ear canal
- Itching
- Hearing capacity becomes subdued or completely diminished
- In severe, advance stage of infection, the pain spread to the head, neck and face and lymph nodes become swollen. High temperature is also accompanied. (1,2)
Causes
- The cause of outer ear infection is due to accumulation of water. The possible reasons of lodging of water in ear cavity are prolonged swimming, faulty swimming technique, in learning period of swimming, faulty shower etc.
- The increase moisture in the ear canal is good culture media for growth of the microorganisms.
- Bacterial and fungal infection is most common types of outer ear infection.
- The bacterial or fungal infection invades the thin lining of the skin and infection is progressed.
- Excessive moisture inside the ear canal cause irritation and scratching can cause injury, which is progressing to infection. (1,2,3).
Diagnosis
ENT specialist usually detect the outer ear infection by discussing the symptoms and then diagnose the outer ear infection by using an otoscope. Otoscope is used for physical examination of the patient’s ear.(1)

Treatment
The provided treatment aim is to control the infection and healing of the ear canal.
Clean-up
Ear canal has a very narrow diameter, therefore it is important to ensure that the topical use ear drops should reach to the affected site. For this cleanup of the ear canal is the first step to follow, specifically if the discharge or pus is accumulated in the ear canal. This is to advise, do not use any sharp thing to clean up your ear. Cleanup of the ear should be done in ENT clinic, as a doctor uses an ear curette or suction device to clean up any discharge, pus, flaky skin, clumps of earwax or other debris.
Medicines use for infection
Depending upon the type of infection and severity of the infection, doctors usually prescribe medicine. The prescribed medicine may contain following active ingredients in combination or single therapy.
- Acidic solution for maintaining the ear’s normal antibacterial environment.
- Steroid to diminish swelling
- Antibiotic to battle with bacteria
- Antifungal medication to invade the infection causing fungus. An infection caused by a fungus
- Doctor has also guided the patient or patient representative how to apply ear drop, which is an effective way to reach the medication in the affected site.
Usually the cool temperature of ear drops cause discomfort in the ear. This can reduce by holding the bottle in palm for a few minutes for maintaining the temperature.
Instructions for Ear Drops Administration
- Assistance of others makes more proper ear drops administration than patients can do their selves
- Before administration of the ear, the patient should lie down on side face in such a manner that affected ear should be upper side.
- Sufficient amount of ear drops should be put inside the ear canal
- Patient should maintain the same posture for a few minutes after completion of the administration of the ear drops.
- If the topical medication cannot control the infection, then oral antibiotic therapy may prescribe.
Analgesic medicines
To control the pain, doctors also suggest to take analgesic (painkiller) medicines whenever required. The included analgesics are ibuprofen, acetaminophen or naproxen.
Precautionary measures
- In addition of the above mentioned medications, some precautionary measures help to support the quick healing:
- Avoid swimming or dive
- Avoid traveling by flight
- Don’t put any foreign material like earplug, headphones or hearing aid, as these aggravate pain syndromes.
- Carefully take shower to avoid water lodging in the ear.
Home Remedies
- Before swimming or bathing, put a petroleum jelly coated cotton ball in ear to provide protection of the ear canal, as this helps to prevent the water to accumulate in the ear canal.
- Avoid scratching inside the ear canal, as this exacerbate infection and pain and condition become worse.
- Doctor’s advice should be followed accordingly for quick healing.
- Correct care of the ear can keep away most of the ear infections. (2,3,4).
Referencing
- Joe Bowman (2014); Outer Ear Infection (Swimmer’s Ear); Retrieve from: http://www.healthline.com/health/otitis-externa#Overview1
- Swimmer’s ear (2013); Mayo clinic staffs; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/swimmers-ear/basics/definition/con-20014723
- Swimmer’s Ear; American Academy of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery; Retrieve from: http://www.entnet.org/content/swimmers-ear
- Melissa Conrad Stöppler, (2015); Swimmer’s Ear Infection (External Otitis); Retrieve from: http://www.medicinenet.com/otitis_externa/article.htm
