Microcytosis
What is microcytosis?
Microcytosis is a blood disorder in which the mean blood cellular volume become less than 82 μm3 (82 fL) in adults. This discrepancy often comes under notice in laboratory diagnosis for suspected hemoglobinopathy.
The blood investigation provides the possible abnormalities which are related with microcytosis and this include serum iron, haemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), gene mapping, transferrin, ferritin, iso-electric focal point of the Haemoglobin, HbA2, HbF, inflammatory status. Evidence showed that iron deficiency in the major findings in case of microcytosis. Thalassemia patients also have the greater possibilities to develop microcytosis.
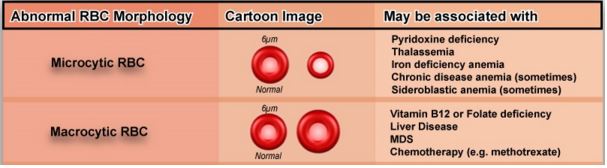
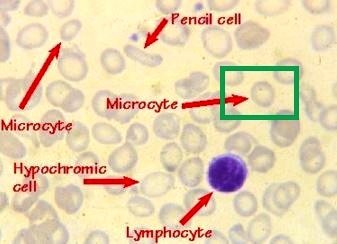
Image 2: Microcytosis
Symptoms of Microcytosis
The major finding of microcytosis is iron deficiency which can be estimated with following symptoms:
- Development of fatigue even after some mild physical activity due to lack of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is made with iron and globin protein and major function is carrying oxygen and nutrients to other tissues. Iron deficiency hamper the production of haemoglobin which leads to hindrance of transportation of oxygen and nutrients and tissues are not get enough energy to perform their function efficiently.
- Lack of oxygen supply leads to shortness of breathing or dyspnoea
- Blood is circulated in blood vessels and under the skin and nails where the blood vessels are spread. In microcytosis, bloods cellular volume decreases and skin and nails bed become pallor.
- Heart pump the blood but due to lack of blood volume heart contract more than the usual to regulate the blood supply but excess contraction leads to systolic murmur.
- One of the major function of RBCs are regulation of body temperature but due to reduction of the mean blood volume leads to increase feeling of cold and hand and feet temperature is usually less than the normal individual.
Causes of Microcytosis
The usual causes of microcytosis are:
Iron Deficiency Anaemia
Usual cause of iron deficiency anaemia is absorption disorder of dietary nutrients in GI tract and mismatches the physiological requirements. This uneven situation occurs when the iron supply is inadequate due to unbalanced diet or physiological need is increased in case of chronic ailments related with GI tract absorption or any blood losing conditions. Iron deficiency anaemia is common with all aged people but most predominant are in young children and menstruating women. Chronic microcytosis in children causes retardation of growth and impaired cognitive health. For pregnant women, microcytosis causes preterm delivery.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is of two types- alpha thalassemia and Beta thalassemia. Alpha and beta are the amino acid chain which bind the structural unit of haemoglobin (heme means iron and globin is protein). The disorder in alpfa or beta chains causes underproduction of haemoglobin and usually associated with severe iron deficiency anaemia.
Sideroblastic Anaemia
In case of adult, heme unit of haemoglobin is produced in mitochondria of bone marrow but in Sideroblastic anaemia the bone marrow unable to produce mature RBCs due to impair heme production in mytochondria.
Clotting Disorders
The clotting disorders like von Willebrand disease, causes delayed blood coagulation and leads to haemorrhage and blood loss which also leads to microcytosis.
Chronic ailments in liver and kidney
Chronic liver and kidney disease causes anaemia. Liver stored vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is essential component in RBCs production but the requirement is very minimal. Liver is supplying vitamin B12 according to the physiological need. In chronic liver ailments, liver unable to perform their function efficiently and insufficiency of vitamin B12 causes under production of RBCs.
Kidney secretes erythropoietin hormone which stimulates the RBCs production but in case of chronic ailments in kidney lack of erythropoietin hormone and decrease the production of RBCs.
Lead and Zinc Poisoning
Lead poisoning leads to reduction of heme production and zinc poisoning causes reduction of iron availability.
Mal-absorption in GI tract
Celiac disease, Intestinal bacterial over growth, H pylori infection, Gastrectomy is the various reason behind the mal-absorption of nutrients in GI tract.
Internal Haemorrhage through GI tract
Gastric ulceration and peptic ulceration, malignancy in stomach, colon or in gut causes internal blood loss.
Heavy Menstrual Flow
Women suffering from heavy menstrual flow due irregular menstrual cycle, post child birth, blood clotting disorder or carcinoma in uterus or other reproductive organ can cause microcytosis.
Blood Donation
Frequent blood donation may causes microcytosis.
Treatment of Microcytosis
For microcytosis, it is essential to know about the underlying cause of the condition. It may be due to nutritional inadequacy or chronic illness. Nutritional deficiency specially iron deficiency can be managed with supplements and if any other co-morbidity causes microcytosis then proper treatment of the diseases condition improves the microcytosis.
Oral iron supplements are easily available in the pharmacy stores and have low cost. The usual side effect is constipation. But severe deficiency or mal-absorption in GI tract may require intravenous administration of drug under medical supervision to monitor allergic reaction.
References
- http://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/1101/p1117.html
- http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/m/microcytosis/symptoms.htm
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8698132
- http://blogs.nejm.org/now/index.php/microcytosis/2011/08/19/
- http://www.gponline.com/clinical-review-microcytic-anaemia/haematology/anaemia/article/1003442
