Hydronephrosis
Overview
Our Urinary system has four parts – the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder, and urethra. Urine is formed as kidneys filter the blood and segregates the waste from the blood. Urine is stored in a part of the kidney called Renal Pelvis. From the renal pelvis, urine flows through the ureter to the bladder.
A one way valve at the bottom of the ureter blocks any urine from going backward up the ureter to the kidney. From the bladder, urine flows out of our body through the urethra. Hydronephrosis describes the swelling of the kidney due to the inability of the urine to drain out.
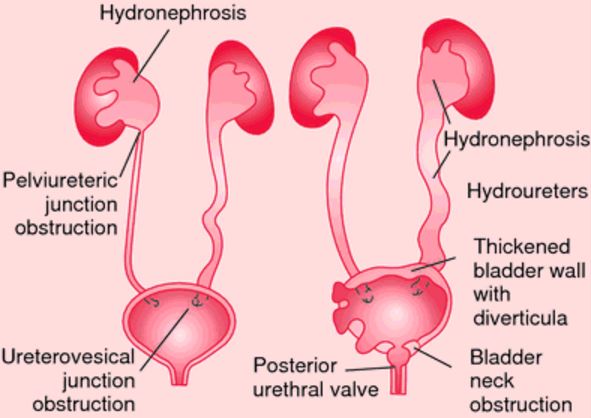
Basically, the urine collecting system of the kidney gets dilated in hydronephrosis. Standing on today 1 out of 100 people are affected by hydronephrosis. It is increasingly getting traces in unborn babies during ultrasound scans. This is known as antenatal hydronephrosis.
Symptoms
There are no specific symptoms for Hydronephrosis. In human body urine flows with minimal pressure while if there is a blockage in urinary tract, pressure can build up and kidney can start to swell and start to press nearby organs as urine is not getting its way out. If treatment is not done in the right time it can cause permanent failure to the kidney’s function.
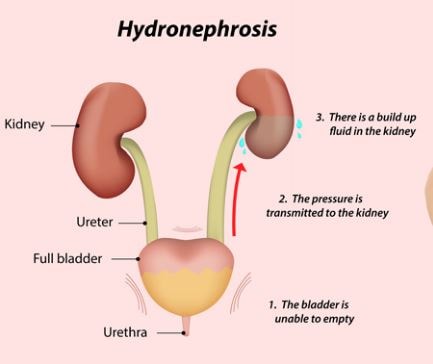
However, symptoms can depend on for how long the urinary tract has been blocked. People with hydronephrosis could have symptoms like urinating more frequently, feeling pressure while urinating. Among other symptoms there are
- Pain in the abdomen.
- Pain while urinating.
- Frequency and urgency of urinating.
- Nausea and the tendency of vomiting.
- Fever.
- Urinary Tract Infection.
- Urine with blood.
- Weak urine stream.
- Swollen kidneys.
Hydronephrosis in babies generally caused no symptoms. But one should consult a doctor if the baby displays possible symptoms of UTI. UTI caused the urine to stay inside the kidney which is why UTIs are most common symptoms of Hydronephrosis.
Types
There can be two types of Hydronephrosis – Unilateral Hydronephrosis and bilateral Hydronephrosis. When one kidney is affected by Hydronephrosis it is known as unilateral Hydronephrosis while if both the kidneys are affected by Hydronephrosis.
Causes
It mainly causes because of the blockage in the urinary tract. If there is a blockage in urinary tract it causes disruption of normal flow of urine and urine starts to build up in kidneys which in turn will stretch the kidneys.
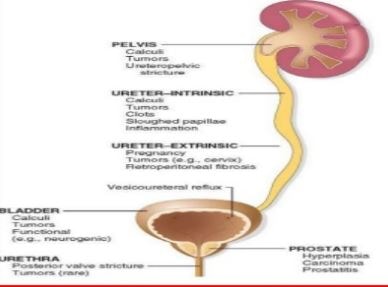
Causes of Hydronephrosis in adults
- Kidney stone – one major reason of hydronephrosis. Sometimes the stones those formed in kidneys can come out of the kidney and block the ureters.
- Due to non-malignant swelling of the prostate gland.
- During pregnancy swollen womb can cause pressure on the ureters.
- Narrowing of the ureters.
- When one or more of the pelvic organs bulge into the vagina.
- Damage to the nerve which controls the bladder.
- Urinary tract cancer.
- Congenital blockage (by birth).
- Blood clot.
- Ovarian cysts.
Causes of Hydronephrosis in babies
Though it is still not clear why unborn babies are affected by hydronephrosis, but in some cases it can be caused by –
- If excess tissues growth becomes abnormal then there can be a blockage in the urinary tract.
- Vesicoureteral reflux – Sometimes the valve that controls the normal urine flow between bladder and ureters doesn’t function properly, causing the urine to flow back up to the kidneys.
Diagnosis
It is suggested that if you are having a problem in your urinary system you should get diagnosed as soon as possible. Long time ignorance to these problems can cause permanent failure of your kidney. For an adult, Hydronephrosis can be diagnosed using an ultrasound scan.
Further tests like blood test, urine test, intravenous Urography, CT scan, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Cystoscopy can be done to diagnose it. While for babies ultrasound scans are done to diagnose Hydronephrosis. Ultrasound scans with a regular interval during pregnancy is solicited.
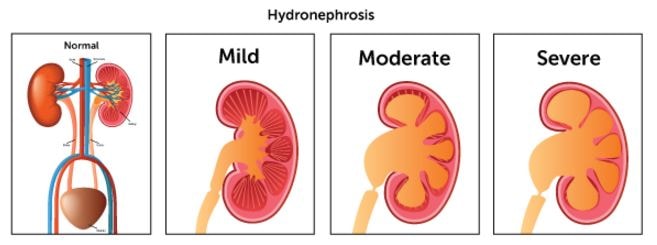
Hydronephrosis – Mild, Moderate & Severe Varieties
Treatment
The goal of the treatment for Hydronephrosis is to make the urine flow normal. As a preliminary care for the patient, it is aimed at minimizing the pain and preventing the infections. As to achieve this, the first stage is to drain the urine out of the kidney.
Some cases can be treated without surgery while some need one. Antibiotics are enough for the infections. For kidney stone surgery is preferable. An enlarged prostate can be treated with medicines or surgery can be done to remove some portion of the prostate gland.
Narrowing Ureter can be treated by inserting a stent, a hollow plastic tube which offers the urine to flow without getting blocked in the narrow section. If the blockage is severe, the excess urine is removed using a catheter or a special tube called a nephrostomy that drains urine from the kidney.
In cases where cancer caused hydronephrosis, usual cancer treatments are required. It caused due to pregnancy need no surgery or any treatment. It gets healed automatically after giving birth.
Complications
If not diagnosed soon enough or if not treated hydronephrosis, the increasing pressure may cause the kidney failure or even death. It is curable, but it should be diagnosed at an early stage. Even if the obstruction or blockage lasts for 6 weeks after the treatment the kidney functions perfectly well.
Though it is found in one person out of every 100 it is not deadly. But negligence can make the situation different. It is suggested if any symptoms of UTI are there better to diagnose for Hydronephrosis.
Pictures
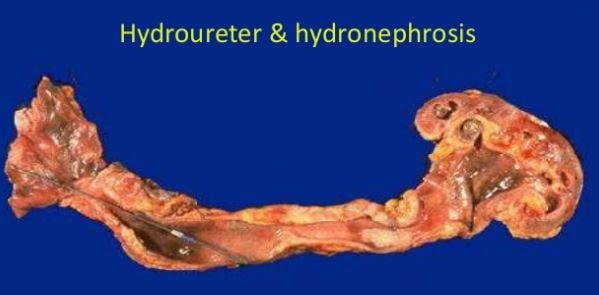
Gross Appearance of Hydroureter and Hydronephrosis
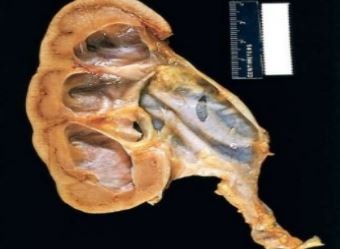
Dilatation of Pelvicalceal System
References
- http://www.healthline.com/health/unilateral-hydronephrosis
- https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/hydronephrosis
- http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Hydronephrosis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- http://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/hydronephrosis
- http://radiopaedia.org/articles/grading-of-hydronephrosis
- https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000506.htm
- https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000474.htm
