Golfers Elbow
What is golfers elbow?
Golfers elbow is the painful inflamed condition affected on the bony bump present at the interior of the elbow joint, where the forearm attached with the upper arm by flexor tendons. The pain become gradually exude to forearm and wrist.
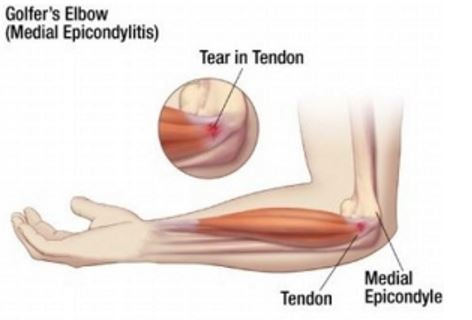
The name of the condition though denoted golfers, but can develop to anybody. The pain is occurs due to overuse of wrist joint or gritting of fingers.
The alternative name of this condition is medial epicondylitis. The golfers elbow is comparable with tennis elbow, which develops at the outer part of the elbow. This is not a permanent damage of the muscles or tendons, adequate rest and treatment can help to full recovery (1,2, 3).
Symptoms of golfers elbow
Pain is the major symptom of the golfers elbow: The pain is felt at the center of the bony knob present inside the elbow. The specifications of pain are as follows:
- The onset of pain is sudden, but extends for longer period
- Pain is worsened with certain activities, which include twisting of the wrist during dangle of racket or golf stick, griping of a ball, shaking of hands, swing of door knob, lifting of weight and pick up anything by moving the palm to downwards.
- The forearm become stiffen
- The griping of hand become weak
- Tingling sensation
- Numbness also develops (2, 4)
Causes
Continual stress can cause damage in the tendon and muscles attached to the forearm. The damage can also occur due to sudden wrong technique of weight lifting, throwing or spinning. The improper training or inadequate warm-up, before staring any throwing activity can also cause tearing of the flexor tendons.
Some sports activities have a higher tendency to develop golfers elbow including:
- Golf
- Javelin, basketball and football, the sports where forceful throwing is the main activity
- Badminton or tennis
- Wight lifting
Some occupational hazards also cause Golfers elbow like
- Plumber
- Painter
- Cook
- Butchers
- Continuous typing on computer
- Line man
In above all the activities need repeated use of the forearm, which damage the soft tissues (1,2).
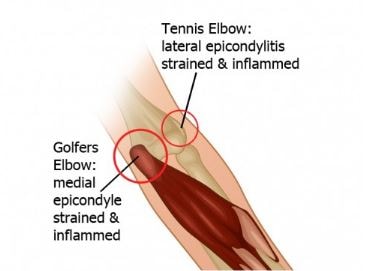
Image 2 – Golfers Elbow Vs Tennis Elbow
Treatment
The quick initiation of treatment can help to overcome the golfers pain at its early stage. The following treatments can help to treat golfers elbow:
- Ice compression: Take some ice cube in a cotton wrapper for avoiding the direct contact and place it over the elbow. This should apply for 3 -4 times a day for reduction of pain and inflammation.
- Providing rest to the elbow joint: Avoid the activities which need much movement of hands and allow to rest the forearm as much as possible. The wearing of splint or strap allows to prevent movement of the affected joint.
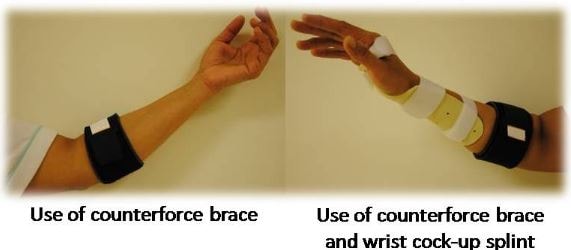
Image 3 – Use of Splint in Golfers elbow treatment
- Non-steroidal- anti-inflammatory drugs are available in pharmacy store as OTC products. These medicines help to reduce the inflammation and pain of golfers elbow.
- In case of severe pain, a local anesthetic injection at the site of pain is also recommended for controlling the pain for a short duration of time.
- Physiotherapy can be beneficial, as this therapy helps to stretch the affected muscles in a proper direction, which is beneficial for pain and inflammation of the golfers elbow (2,3,4).
Surgery
elbow arthroscopy is the novel surgical process recommended for those who are not get benefits by non surgical therapies. During elbow arthroscopy, the bone spurs, which is developed due to overuse can be removed and also loose-fitted fragments of cartilage if present at the injured side is also corrected. The surgery usually conducted under general anesthesia, but sometime regional nerve block injection is preferred to conduct the surgery.
During surgery, an arthoscope, a camera like structure, inserted into the affected elbow by small incision. The images of the camera are displayed on a monitor and guide the surgeon for conducting the removal of the bone spur and reset the joint. As the surgery need not to open the joint with big cut, so the surgery related complications and recovery period is less (5).
Exercises
- Active motion of the wrist, including flexion and extension: At the beginning, the affect wrist should bend in forward and backward direction as much as possible, repeat this stretching exercise for 2 rounds. Each round should have 15 times, forward – backward bending.
- Stretching of wrist: Pressing of the affected hand with other hand at the backward direction. Hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and then release the pressure. In the next step, stretch the fingers in backward direction by pressing the fingers. Hold the pressure for 15 to 30 seconds and then release the pressure.
- Pronation and supination of the forearm: The affected elbow bends by making 90 degrees at the center of the body. The direction of the palm is at the initial stage in an upward direction for 5 to 8 seconds and then move the palm downwards and hold the position for 5 to 8 seconds. Continue this by making two cycles, each one should have 15 movements.
- Strengthening of grip: Pressing a soft rubber ball and grip for compress for 5 seconds. continue this for two rounds and each round should contain 15 cycles of squeezing (6).
References:
- Dennis Ogiela (2014), Medial epicondylitis – golfer’s elbow; Retieve from: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/007638.htm
- Mayo Clinic staff (2015); Diseases and Conditions – Golfer’s elbow; Retieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/golfers-elbow/basics/definition/con-20027964
- Dr Rob Hicks (2015); Golfer’s elbow: Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment; Retrieve from: http://www.webmd.boots.com/fitness-exercise/guide/golfers-elbow-basics
- John Miller; Golfers Elbow; Retrieve from:http://physioworks.com.au/injuries-conditions-1/golfers-elbow
- Jay D. Keener (2012), Elbow Arthroscopy, Retrieve from: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00646
- RelayHealth; GOLFER’S ELBOW EXERCISES; Retrieve from: http://www.summitmedicalgroup.com/library/adult_health/sma_medial_epicondylitis_exercises/
