Circumoral Cyanosis
Definition of circumoral cyanosis?
Circumoral cyanosis can be defined as bluish shade develop to the surrounding skin of the lips. Usually bluish tint is quite common in neonates, because their skin structure is very thin. Therefore, the blood vessels which lies just beneath the skin are well seemed superficially.
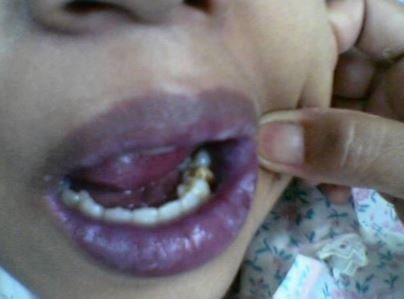
Image – Bluish discoloration around lips
Veins are blue in color and present surrounding of lips just below the skin and close observation helps to find blue shading most of the time. Normal blood circulation can cause pink-red flesh tone blood circulated through arteries.
The blood circulation is reduced at surrounding area of the lips for different reasons and blue shade is prominent due to presence of veins. If this shade extends to the lips, then it need immediate medical assistance, as it is an emergency situation.(1)
Symptoms of circumoral cyanosis
- Breathing difficulty. This is very critical symptom, which must be monitored, when a bluish shed develops around the lips for ensuring breathing is properly taken place in new born child.
- Anorexia or loss of appetite
- Tetchiness
- Murmur sound with buzz noise
- Unable to move due to excessive fatigue (4)
Circumoral Cyanosis Causes
The oxygenation or supply of oxygen is considered as a vital sign for neonates, which is essential to monitor. The cyanosis is directly affected skin color.
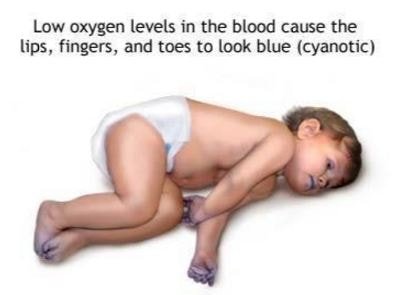
Source – Adam Inc
The possible reasons of Circumoral cyanosis in neonates are as follows:
Cyanotic Heart Disease
This can develop with the following conditions:
- Obstruction in the pulmonary blood flow and this clinical condition is associated with critical pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia and Tetralogy of Fallot.
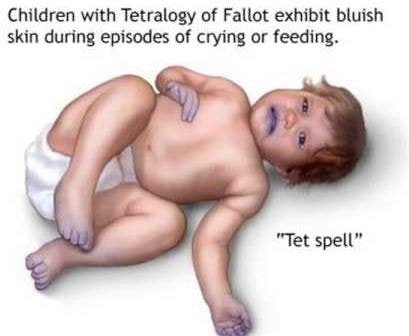
Image 3 – Tet Spell during crying or feeding
Source – Adam inc
- Dissonant between arterial- ventricular connections and medically termed as transposition of great arteries.
- Single ventricle, tricuspid atresia and truncus arteriosus are various clinical conditions where mixing of blood in heart is common sign.
Primary Pulmonary Disorders
This can develop with following conditions
- Congenital pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome or meconium aspiration syndrome is develop due to Parenchymal disease. Respiratory distress syndrome is also known as breathing disorder and meconium aspiration syndrome occurs due to a mixture of meconium and amniotic fluid breathing, meconium is present into the lungs about the time of childbirth. Both the conditions are affected neonates.
- Congenital diaphragmatic hernia is associated with defective diaphragm in newborn or pneumothorax means air entrapped between lungs and chest cavity, are the example of extra parenchymal diseases.
- Persistent pulmonary hypertension (PPHN ) is defined as the malfunction of the regular circulatory alteration that arises after delivery.
- Asphyxia or insufficiency of oxigen, severe polycythemia, abnormally high range of RBCs or Methemoglobinemia or higher content of methaemoglobin in the blood are other associated condition cause circumoral cyanosis. (2)
The above mentioned cause are mainly affect new born, other than these following conditions are generally affect
- Circumoral cyanosis is also occur due to carbon mono-oxide poisoning, in which low oxygen content in the environment and cause breathing difficulty and insufficiency of oxygen supply in the body tissues.
- Epiglottitis, bronchitis and shock can cause circumoral cyanosis.
- Other than these, too much cold weather or high altitude also cause circumoral cyanosis (4).
Subdivisions of cyanosis
A medical subdivision is made to understand the severity of the cyanosis – central cyanosis and peripheral cyanosis. in both the conditions circumoral cyanosis is observed. Central cyanosis is associated with cardiovascular disorder and peripheral cyanosis arises with lung disorder. (3)
Diagnosis
- If circumoral cyanosis is noticed, then immediate medical assistance is required, though presence of other symptoms are not present. The initial diagnosis is started with physical examinations, which help to identify the type of cyanosis. If only circumoral cyanosis is noticed, then it is not a serious health issue, but associated symptom development can be fatal.
- Airway, Breathing and Circulation (ABC) must be checked by the healthcare professionals.
- Pulse oxymetry is conducted to diagnose central cyanosis. (2,3,4)
Treatment
The following treatment processes are applied to treat circumoral cyanosis:
- Initial first aid care must be provided to stabilize ABC.
- Administration of supplementary oxygen may require to restore ventilation or need to assist ventilation. Oxygen supply can help to maintain the continuous positive airway pressure.
- Metabolic acidosis is treated with bicarbonate therapy for maintaining the internal pH level.
- Management requires for managing hypothermia
- Antibiotic therapy is prescribed to reduce infection. (2,4)
Reference
- Joe Matusic (2006), CIRCUMORAL CYANOSIS; Retrieve from: http://www.babymd.net/pocyanosis.htm
- Theresa Bowden (2013), Cyanosis and the Road to Diagnosing Congenital Heart Defects; Retrieve from:https://www.nwmedstar.org/uploadedFiles/Services/Education_and_Outreach/Provider_Chats/2011-2012/Cyanosis%20and%20the%20Road%20to.pdf
- Peter Peters (2014), Designing preterm neonatal cyanosis simulation; Retrieve from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261557431_Designing_preterm_neonatal_cyanosis_simulation
- Child with Blue Lips (2014); Retrieve from: http://www.newhealthguide.org/Child-with-Blue-Lips.html
