Vaginal Warts
What is vaginal warts?
Most of the vaginal warts are the resultant of the sexually transmitting infection. The sexually active women often get vaginal warts at the opening of the vagina. The infection is caused by certain types of Human papilloma virus (HPV). This is a contagious infection like other sexually transmitted disease and unproductive sexual intercourse can spread the infection to partners. Males can also potential to develop genital warts. (1,2,3)
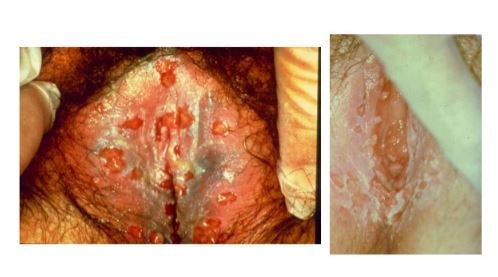
Symptoms
Vaginal warts commonly develop in the opening of the vagina or on vulva, cervix and sometime extends up to urethra and anus. The included symptoms are as follows:
- Vaginal discharge is a common symptom.
- The warts are painless, but may provide itching or burning sensation.
- during sexual intercourse rarely bleeding occurs.
Sometimes, vaginal warts cannot seen by the naked eye, but it provides the feeling of bumps on the skin. The vaginal warts are sometimes grow in a cluster and becomes large masses. If vaginal warts extended or enlarged, then the condition become severely painful and uncomfortable. (1,3,4)
What do vaginal warts look like?
Usually, vaginal warts look like a reddish pink colored flesh, soft touching skin bumps and some warts are having cauliflower like upper surface. (1)
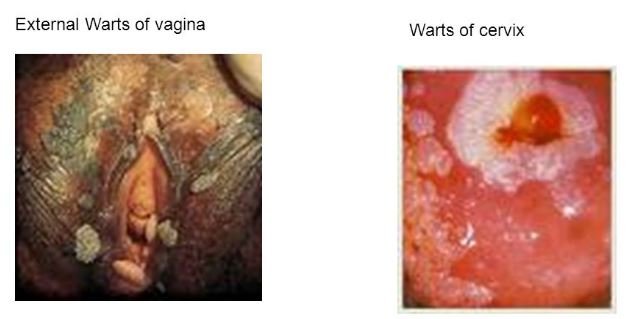
Causes
Human papilloma Virus (HPV) is the main culprit to develop vaginal wart. Almost 100 different types of HPV are present and cause various types of infections. Researchers revealed that HPV-6 and HPV-11 are responsible for wart formation and HPV-16 & HPV-18 are responsible for the development of the cervical cancer. Therefore, usually vaginal warts does not cause of cervical cancer, as the viral strain is differ. But the untreated condition may cause severe multiple strain infection and transform into cervical cancer.
The mode of transportation and spreading of HPV is through skin to skin contact, which include sexual intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or any other contact that involves the genital area. Sometimes the infection is asymptomatic, but can act as a carrier. Even in initial treatment stage, individual with vaginal warts can cause transmition of the HPV virus.
Warts can develop after one week of the onset of infection, but sometimes it can appear after one year also. It is very difficult to evaluate how or when infectious agent enter into the victim’s blood. (1, 3)
Risk factors
Most of the sexually active women have vaginal warts, as they infected with HPV at least once in their life span.
The factors which increase the risk of infections are
- Without condom or unprotected sexual intercourse
- Multiple sex partners.
- Already have other types of STD (Sexually transmitting infection)
- Partner has genital warts and does not share the truth
- Sexually active at a young age. (3)
Complications
The most common complications associated with vaginal warts are cervical cancer development. Other associated cancer can develop on the vulva, anus and sometimes it can also cause mouth and throat cancer. It is not necessary that HPV always cause cancer, but it is recommended that PAP smear test can regularly conducted to check the clinical status.
Other than this, vaginal warts may create problems during pregnancy. If the wart size becomes enlarged, then it causes difficulty in urination. Vaginal warts can reduce the stretching ability of the vaginal wall during delivery. Larger size warts can cause bleeding during childbirth.
In rare cases, mother with vaginal warts can give birth of a child, who has congenital throat warts. Surgical removal may prescribe by the doctor, if the warts cause blocked of the child’s airway. (3)
Diagnosis
Vaginal warts diagnosis is difficult, if the warts are not seen by the naked eye. Another factor is that women may feel hesitant to talk about vaginal warts. However, for diagnosis purpose, doctors need to discuss the symptoms and then conduct the physical check up. Thorough knowledge of the medical history also important. If the doctor suspects the presence of infection, then some confirmatory test is conducted for determining the presence of infection.
Further, to become a safer side usually doctors order for biopsy. In a biopsy, a tissue sample is collected from the warts or suspected area and conduct laboratory tests, this helps to detect any malignant tissue present in the warts or not.
With regular interval PAP smear test is conducted for diagnosing the HPV and reduce the further risk.(1, 2,7)
Treatment
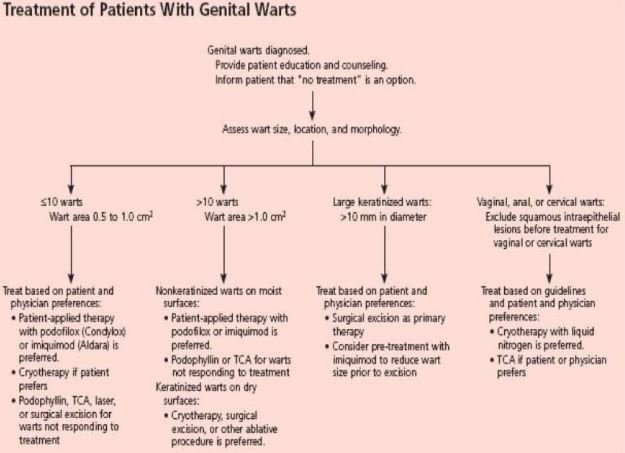
Usually the vaginal warts go way in their own way with time, though the infected virus present in the blood stream, so the warts reappear at any time. For treating symptoms is important to reduce the discomfort.
Over the counter medicines available in the pharmacy store for warts removal are not effective to treat vaginal warts. Doctor can prescribe some topical medicine for treating vaginal warts, which include:
- Condylox (podophyllin and podofilox)
- Aldara (imiquimod)
- TCA (trichloroacetic acid)
The visible vaginal warts can be removed by surgical intervention. The different surgical interventions include:
- Laser rays treatment,
- Electrocauterization or burning,
- Cryotherapy or freezing, or
- Incision of vaginal warts
Other than these, injection of interferon is another option to treat vaginal warts. The following precautionary measures should be taken after the wart removal process:
- Maintain the proper hygiene at the genital organ
- Avoid scratching at the treated area
- Evade sexual intercourse for a certain period
- Follow the hand washing technique after touching the warts
- Cold compression at the site of the warts can help to reduce the associated discomfort
- Take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to relieve pain. (4,5)
How to get rid off of vaginal warts?
The following are preventive measures, which help to rid off vaginal warts:
Gradasil or other available HPV vaccine can help to defend women from responsible HPV strains, which cause vaginal warts and cervical cancer. Another vaccine, Cervarix specifically offers protection from cervical cancer, though it is ineffective against vaginal warts.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices suggests to get HPV vaccinations for girls between the 11 and 12 years of their age. This vaccine is effective up to 26 years age of the women. The vaccine should be taken prior to become sexually active, as this vaccine is potentially active when an individual does not expose to HPV.
It is always advisable protective sexual contract or use condoms during sexual intercourse, though you are already vaccinate with the HPV vaccine. (5,6)
References
- Daniela A Carusi, Patient information: Genital warts in women (Beyond the Basics) (2015); Retrieve from: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/genital-warts-in-women-beyond-the-basics
- Traci C. Johnson, (2015); Understanding Genital Warts — the Basics; Retrieve from: http://www.webmd.com/sexual-conditions/hpv-genital-warts/understanding-genital-warts-basics
- Mayo Clinic Staff (2014); Genital warts; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/genital-warts/basics/complications/con-20019380
- Genital Warts (2014); Retrieve from: https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/stds-hiv-safer-sex/genital-warts
- Genital Warts; Retrieve from: http://www.healthline.com/health/std/genital-warts#Overview1
- By Mayo Clinic Staff (2012); Genital warts; Retrieve from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/genital-warts/basics/definition/con-20019380?p=1
- Types of Genital Warts; Retrieve from: https://www.dred.com/uk/types-of-genital-warts.html
