Mottled Skin
What is mottled skin?
Clinically mottled skin is defined as the condition with irregular painless patches develop on the skin. The patches are developed due to alteration of blood vessels present beneath the skin. Although this patch does not produce any physical discomfort, but it affects mental well-being and individual with mottled skin often suffers from psychological distress (1).
Associated symptoms
The mottled skin does not produce any pain or associated discomfort, but the following specifications are the specific for mottled skin:
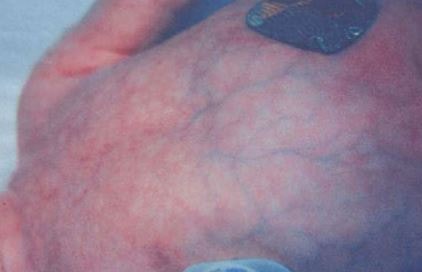
- The patches are in different shapes and size and present on the surface of the skin
- The color of the patches may vary, including red, dark brown, brown, purple or greenish. Usually the initial color of the patches is red and later it turns to brown, purple or greenish.
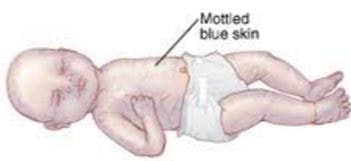
- The discolored patch may develop in nose, lips and genital area for children and infants (2,3).
Causes
The vascular constriction of the blood vessels, which are sited beneath the skin can cause mottled skin. There are various reasons for altering vascular structure and following are the common reasons:
- The temperature of the body is fluctuated
- Increasing with age
- Blood disorders
- Administration of anti-coagulant therapy
- Reduction of platelet count
- Fair skin persons are more prone to mottled skin, though dark skinned persons can also develop mottled skin, but that are less prominent.
- If the skin structure is very translucent, then mottled skin is more prominent.
- Excessive exposure to the day sunlight can cause over pigmentation and causes mottled skin.
- The onset of mottled skin in infants or childhood may due to over stress of mother during pregnancy and childbirth. This marks usually remove with increasing of age of the infant. Cutis marmorata is the term used for infant’s mottled skin.
- Immature vascular bed causes mottled skin in children.
The following conditions also cause mottled skin:
- Corynebacterium minutissimum bacteria causes skin infection, term as Erythrasma can cause mottled skin.
- Estrogen and progesterone are the two hormonal alteration with prolonged sun exposure can cause mottled skin in female.
- Genetic disorder can cause the onset of neurofibromatosis, which provides symptom of Cafe-au-lait spots and mottled skin is a chrecterised feature of this disorder.
- Birthmark like Mongolian spots can cause mottled skin.
- Hypopigmentated skin is developed due to Pityriasis alba can cause mottled skin.
- Different types of skin disorders like eczema and ringworm can cause mottled skin.
- Radiation therapy can cause skin discoloration.
- Vitiligo is the condition which is developed due to loss of pigmentation.
- Melanoma is a type of skin cancer, which is also caused mottled skin. (3,4)
Differential diagnosis
- Physical examination and detail discussion of symptoms are very important to diagnose the underlying cause of the mottled skin.
- Thorough knowledge of medical history is also an important step of diagnosing the underlying cause of mottled skin.
- The following laboratory tests are also ordered for diagnosis:
- Microscopic examination of skin tissue. For this skin sample is collected from the lesion and prepared slide in the laboratory and examine the histology of the skin tissue.
- Skin biopsy
- Ultraviolet light testing or Wood’s lamp examination of the skin. (4, 5)
Treatment
Treatment for mottled skin can be two types:
- Home remedy
- Pharmacological treatment
Home remedy
- Avoidance sun exposure.
- Application of sunscreen lotion with SPF 30. This can prevent sunburn and treat hyper pigmentation.
- Topical application of prescribed antimicrobial lotions such as ketoconazole, Selenium sulfide or tolnaftate helps to prevent ringworm, eczema or related dermatological infection.
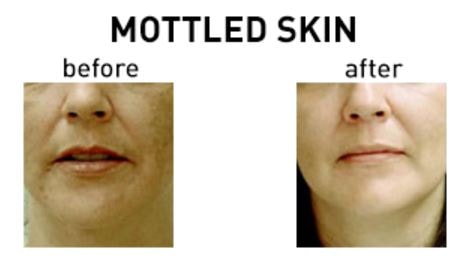
- Beauty treatment such as application of bleach can help to lighten the skin marks.
- Some cosmetic products can hide the skin marks, but this does not provide permanent recovery.
- Cold exposure may worsen the condition, so protective wearing is necessary in cold weather.
Pharmacological treatment
The pharmacological treatment should be conducted under supervision of a dermatologist in proper clinical set up. The treatments are as follows:
-
Chemical peels
The chemical peeling therapy is conducted by applying some chemicals to exfoliate skin. The duration and technique for the treatment vary depending upon the dark coloration of the skin. The treatment can conducted for 24 hours to 6 months or more duration. Deep, medium or superficial application of chemical peel therapy is available and choosing of therapy option is depending upon the patient condition and dermatologist decision.
-
Photorejuvenation
In this therapy, light rays pass to the deep layer of the skin to enhance the re-growth of the skin tissue for rejuvenating the skin cells and diminish the mottle skin.
-
Laser resurfacing
Laser rays are applied to the subcutaneous or cutaneous layer of the skin for resurfacing and treat the mottled skin (2,3,4).
References
- What is mottled skin; Retrieve from: http://www.wisegeekhealth.com/what-is-mottled-skin.htm
- Mottled Skin (2015); Retrieve from: http://minimemedia.com/mottled-skin/
- Causes Of Mottling Of The Skin: Symptoms And Treatment Options (2012); Retrieve from: http://www.tandurust.com/skincare/mottled-skin-causes-treatment.html
- Richard J. Moskowitz (2014); Skin color – patchy; Retrieve from: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003224.htm
- Kevin Berman (2012); Skin color – patchy; Retrieve from: http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/symptoms/skin-color-patchy/overview.html
